Understanding the China Business Landscape
China's coffee market presents a complex landscape of opportunities and challenges for Starbucks. The country's growing middle class and increasing appetite for premium coffee experiences have driven significant market growth. However, this promising scenario is tempered by intense competition and rapidly evolving consumer preferences.
The competitive environment in China has intensified dramatically in recent years. Local players, particularly Luckin Coffee, have emerged as formidable rivals, challenging Starbucks' once-dominant position. Luckin's aggressive expansion to over 13,000 stores, surpassing Starbucks' nearly 7,000 locations, underscores the fierce battle for market share.
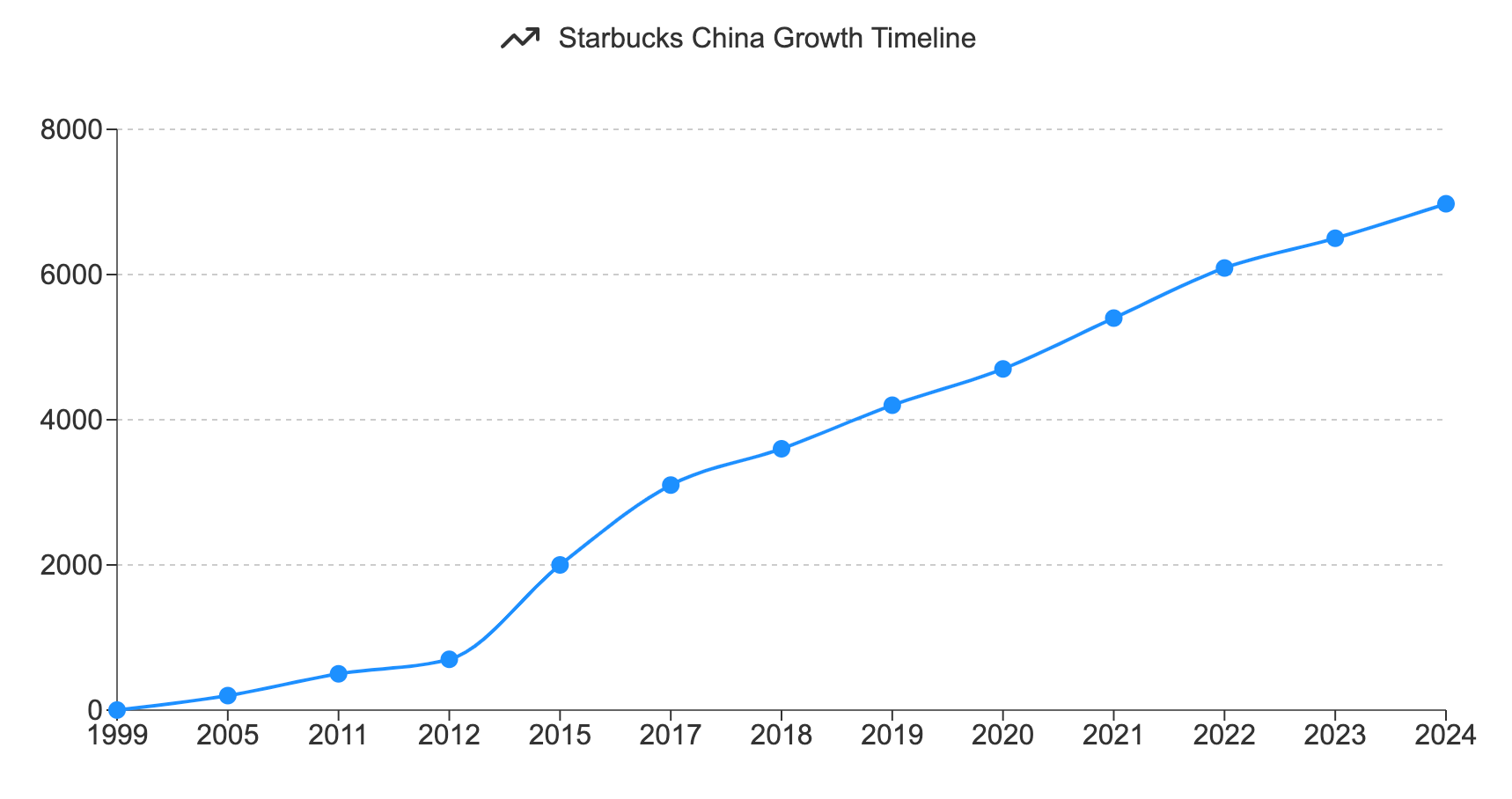
Starbucks' long-standing presence in China since 1999 has allowed it to build strong brand recognition and customer loyalty. However, this historical advantage is being tested by nimble local competitors and changing consumer tastes. The company's recent performance in China, marked by slower-than-expected growth and market share challenges, indicates that past success does not guarantee future dominance.
China remains a significant contributor to Starbucks' overall revenue and growth prospects. However, the recent firing of CEO Laxman Narasimhan suggests that the company's performance in this crucial market may have fallen short of expectations, necessitating a strategic reassessment.
"We remain completely committed to our business and our partners in China for the next 25 years and beyond. The long-term opportunity for us is significant."
This statement, made by Narasimhan before his departure, now stands in stark contrast to the current reality, highlighting the disconnect between Starbucks' optimistic projections and the challenges it faces in the Chinese market.
Before you dive into our in-depth analysis, we have a quick request:
If you find this content useful, please consider sharing it!
Why? Your shares help us reach a wider audience, allowing us to continue producing high-quality, comprehensive content like this—completely free, with no paywalls or subscriptions.
Thank you for your support!
Starbucks' Expansion Strategy
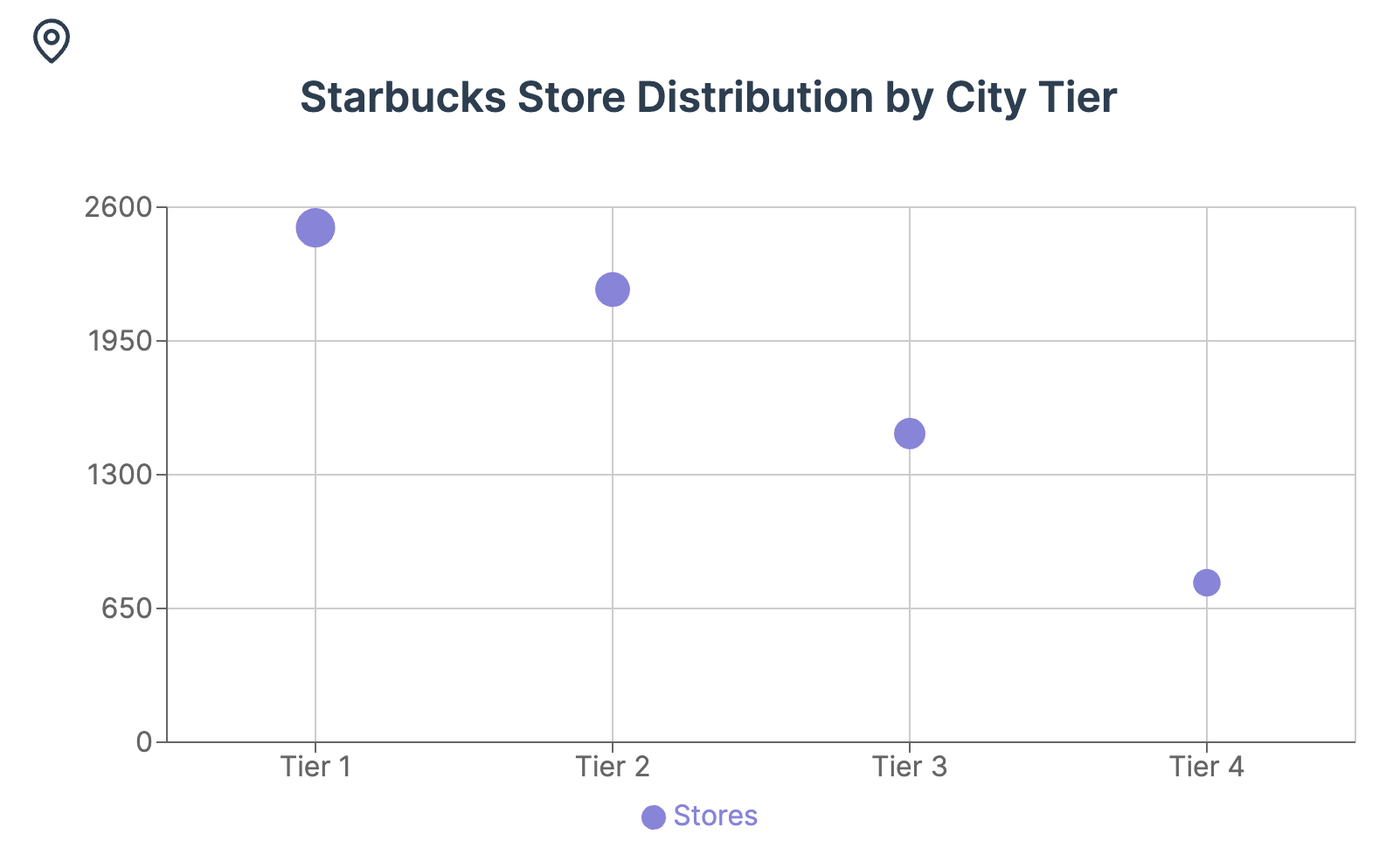
Starbucks has pursued an aggressive expansion strategy in China, aiming to capitalize on the country's vast market potential. The company's goal of reaching 9,000 stores by 2025 demonstrates its ambitious vision for growth. This expansion has primarily focused on Tier 1 and Tier 2 cities, where demand for premium coffee experiences is highest.
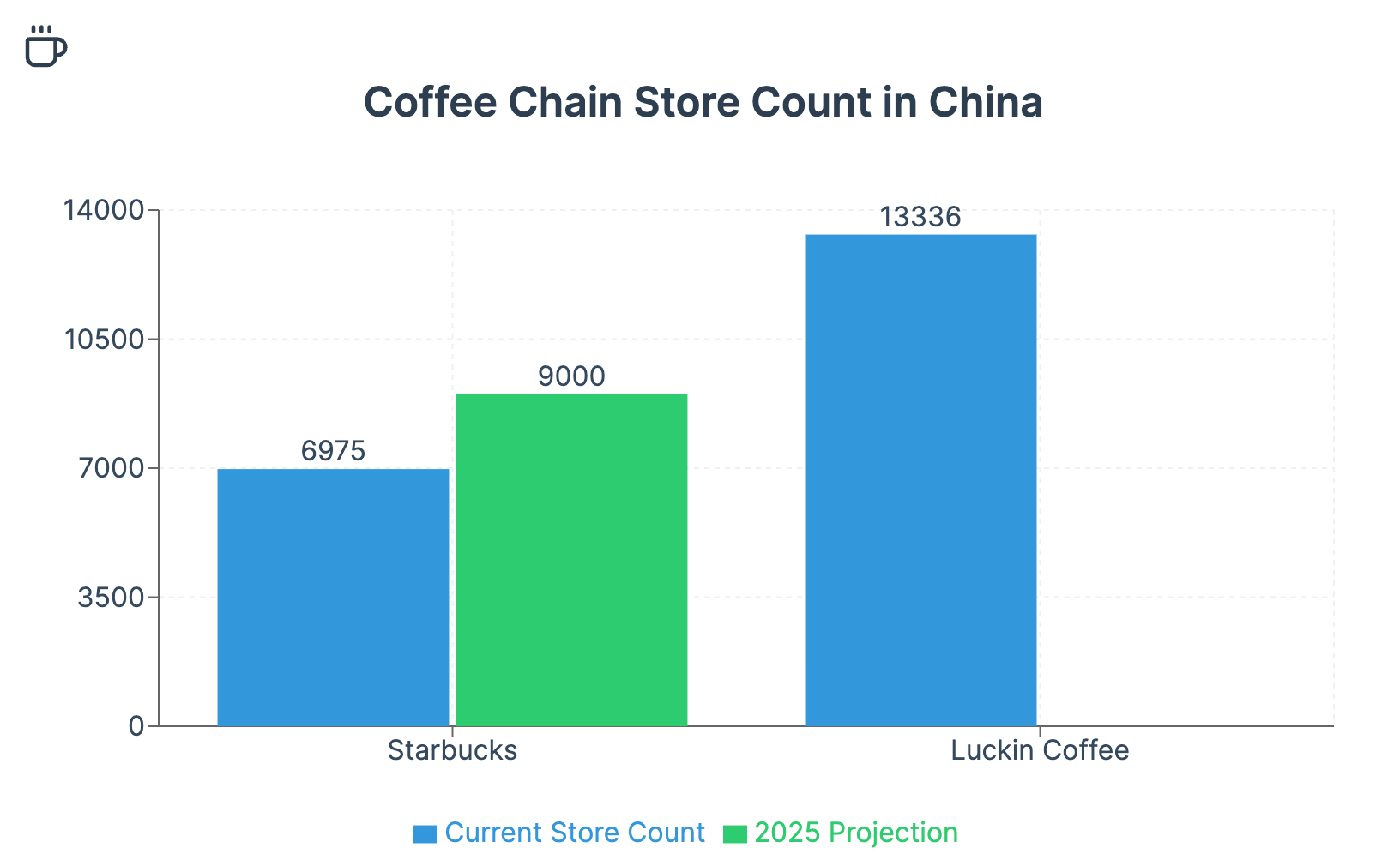
However, this strategy may need reevaluation in light of recent market dynamics. The rapid expansion of local competitors like Luckin Coffee, often at lower price points, challenges Starbucks' premium positioning and may limit its growth potential in certain market segments.
The company's expansion strategy must now balance the need for growth with the realities of a more competitive and digitally-driven market. The new leadership will need to assess whether the current expansion plans are sustainable and whether a more nuanced approach to store openings and digital integration is necessary.

Specialty Coffee Market in China
The specialty coffee market in China has experienced rapid growth, driven by increasing consumer sophistication and a growing appreciation for high-quality coffee. Starbucks, leveraging its global reputation and expertise, has positioned itself as a leader in this segment.
The company has invested significantly in its coffee sourcing and roasting capabilities to enhance the quality of its offerings in China. The Coffee Master program has been instrumental in educating Chinese consumers about coffee and building Starbucks' reputation as a coffee authority.
However, local competitors are quickly closing the gap in terms of coffee quality and variety. Many Chinese coffee chains now offer specialty grade beans and sophisticated brewing methods, challenging Starbucks' differentiation in this area. The company's premium positioning, once a key differentiator, may now be limiting its ability to capture a broader market share, particularly among more price-sensitive consumers.
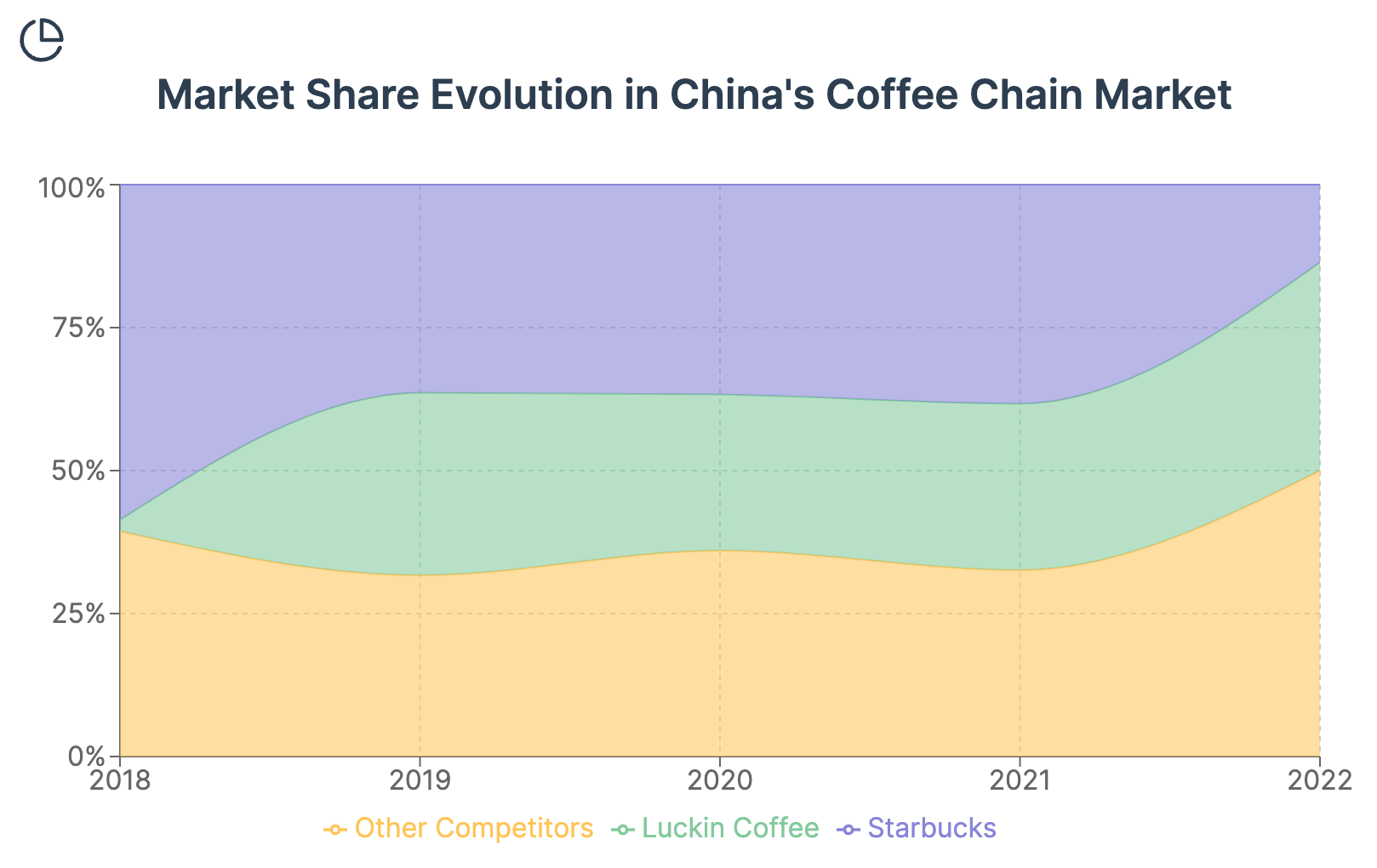
Starbucks must continue to innovate and elevate its coffee offerings to maintain its leadership in the specialty coffee segment. This may involve introducing more localized flavors, showcasing rare and exclusive beans, or offering more immersive coffee experiences to justify its premium pricing.
Market Performance and SBUX Stock
Starbucks' performance in China has significant implications for its overall financial health and stock price. Historically, the company's strong growth in China has been a key driver of investor confidence. However, recent quarters have shown concerning trends, with slower growth and increased competitive pressures.
As of early 2024, SBUX stock traded around $90, with a market capitalization over $100 billion. However, the stock has faced pressure due to underwhelming performance in China. The recent CEO change, while not solely attributed to China strategy, reflects the challenges the company faces in this crucial market.
Investors are closely watching Starbucks' ability to navigate the competitive landscape in China and return to strong growth. The company's success or failure in adapting its strategy to the evolving Chinese market will likely have a significant impact on its stock performance in the coming years.
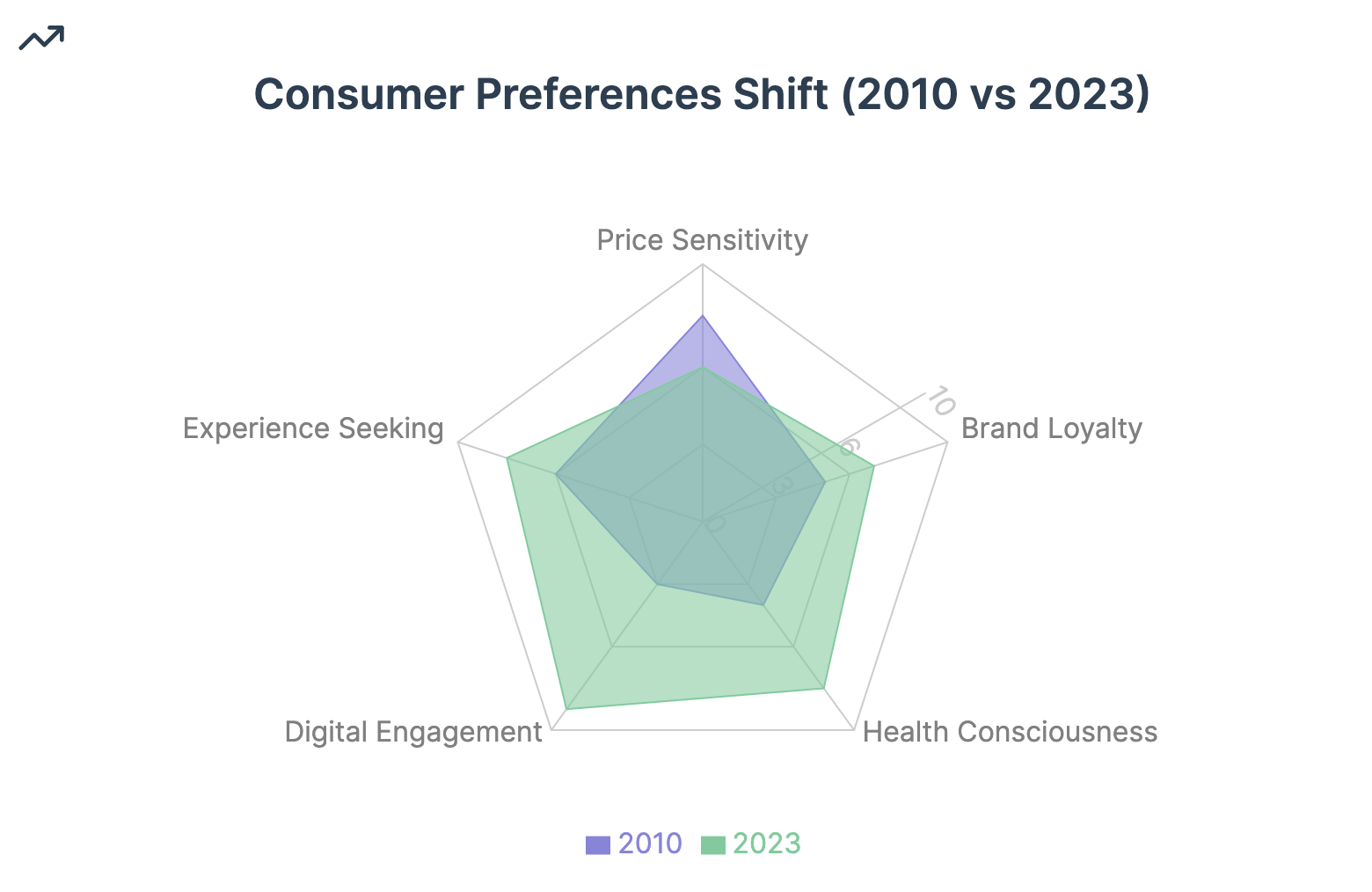
Consumer Behavior and Preferences
Chinese consumers, particularly in urban areas, have shown an increasing appetite for premium coffee experiences. This trend has historically played to Starbucks' strengths, allowing the company to position itself as a luxury brand and lifestyle statement.
Starbucks has successfully tapped into this trend by offering a unique and personalized in-store experience. The company's stores in China are often larger and more elaborately designed than their Western counterparts, serving as social hubs and status symbols for urban consumers.
The Starbucks Rewards loyalty program has been particularly successful in China, driving customer retention and increasing visit frequency. As of early 2023, Starbucks had 20 million Rewards members in China, demonstrating strong customer engagement.
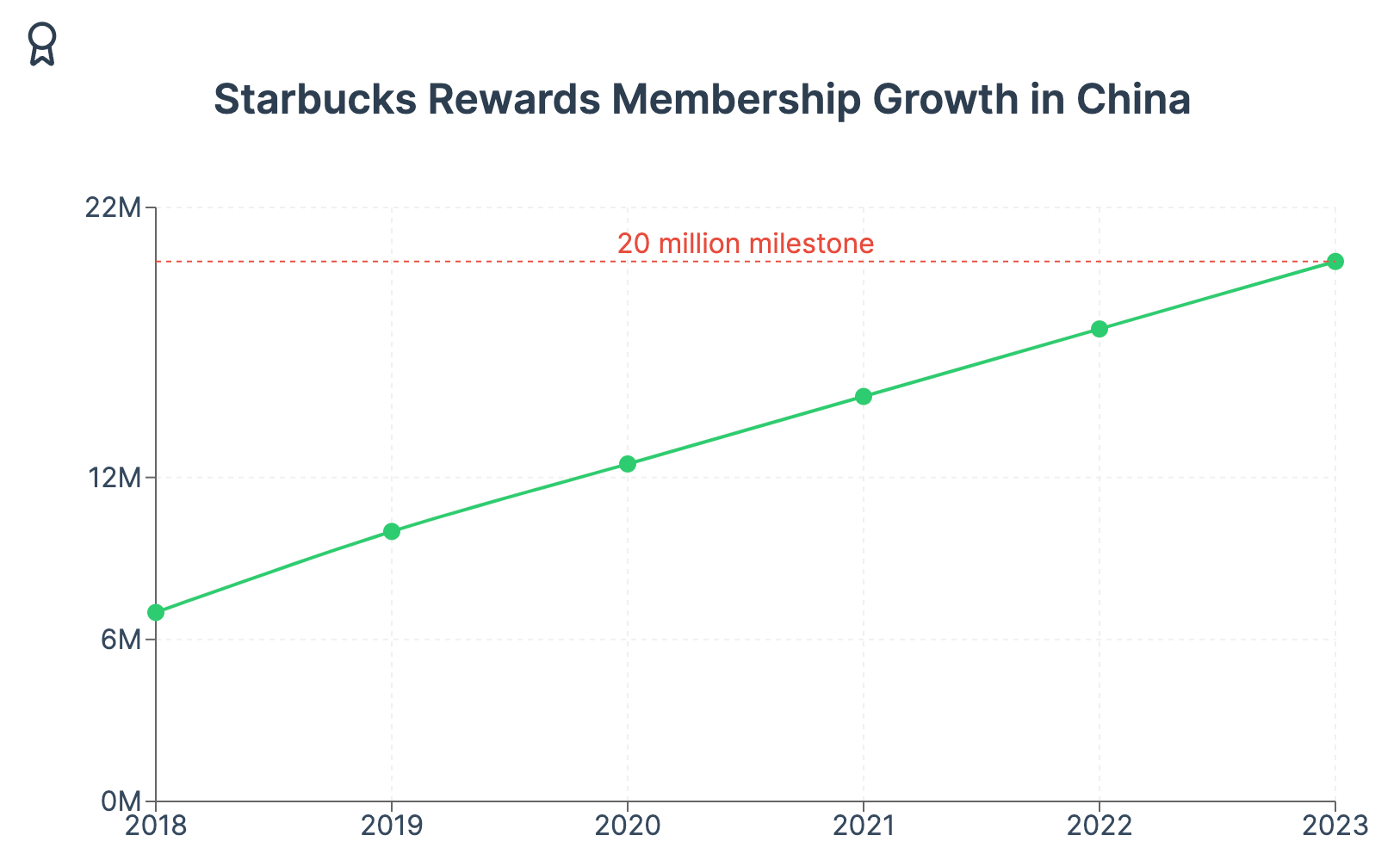
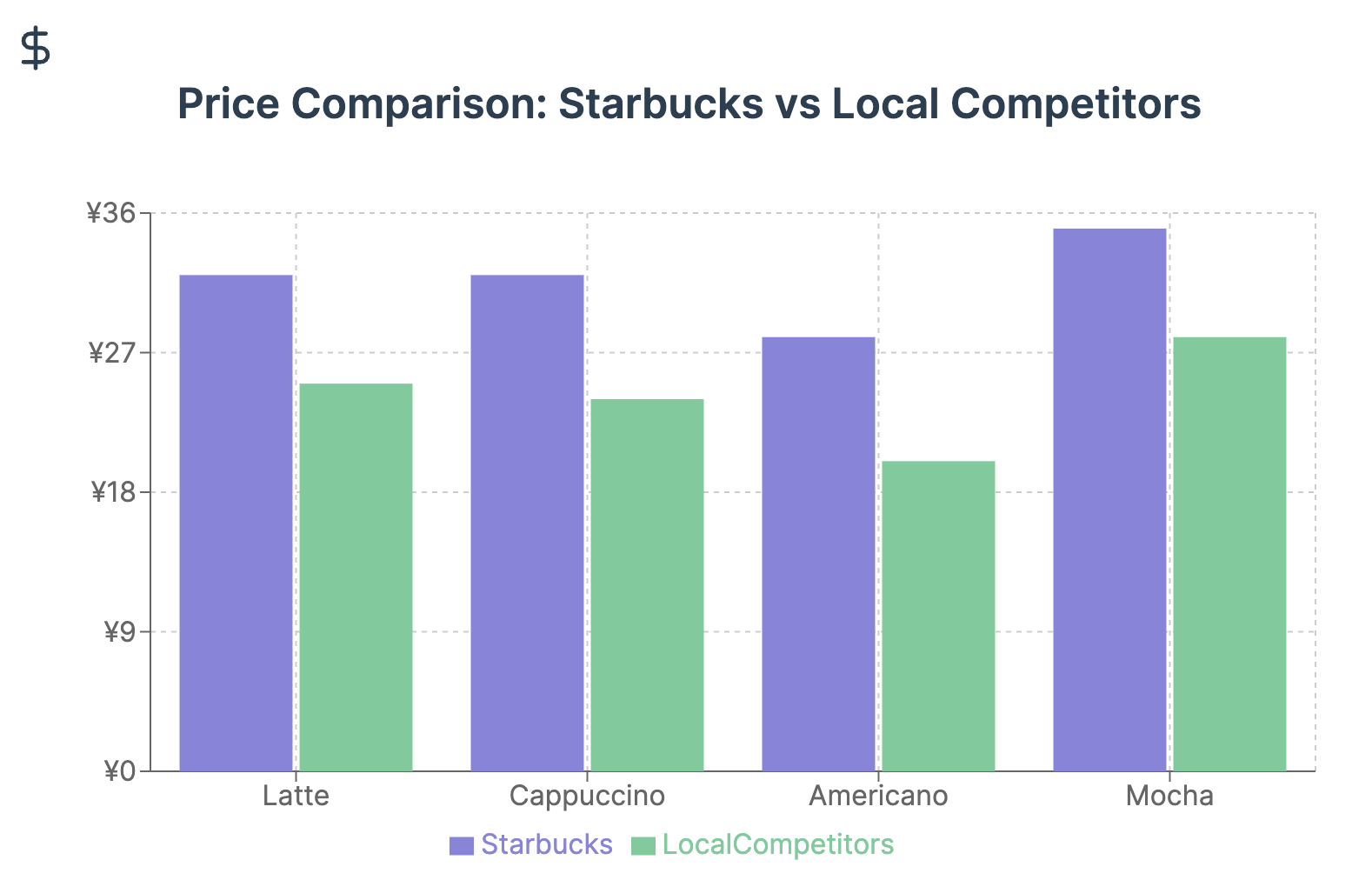
However, Chinese consumers are also increasingly price-sensitive and value-conscious, especially in the face of economic uncertainties. This trend poses a challenge to Starbucks' premium pricing strategy. The company's refusal to engage in price wars, as stated by Belinda Wong, Starbucks co-CEO for China, may prove problematic:
"We're not interested in entering the price war."
This stance, while consistent with Starbucks' premium positioning, may limit its ability to attract and retain more price-sensitive customers, especially as local competitors offer quality coffee at lower price points.
Additionally, Chinese consumers are showing a growing preference for healthier options, including low-calorie and low-sugar beverages. Starbucks has responded to this trend with product innovations, but must continue to adapt its menu to meet these evolving preferences.
Store Experience and Design
Starbucks has invested heavily in creating unique and welcoming store environments in China. The company's stores often feature modern, sleek designs with a focus on sustainability and energy efficiency. Many outlets incorporate local architectural elements and decor, creating a culturally resonant experience for Chinese customers.
The Starbucks Reserve Roastery in Shanghai, opened in 2017, exemplifies this approach. As the second-largest Starbucks Roastery in the world, it serves as a flagship store that showcases the company's commitment to coffee craftsmanship and experiential retail.
Starbucks stores in China typically offer a wide range of seating options and amenities, including free Wi-Fi and power outlets. This "third place" concept – a space between home and work for relaxation and socializing – has been central to Starbucks' appeal in China.
However, the effectiveness of this high-end store experience in driving frequent, everyday visits – crucial for sustained growth – may be diminishing as competitors offer similar amenities at lower price points. The company may need to reassess its store design strategy to balance premium positioning with broader accessibility.
Digital Transformation and E-commerce
Starbucks has made significant strides in its digital transformation efforts in China. The company's mobile app allows customers to order and pay for their coffee online, with options for delivery or in-store pickup. This digital ecosystem has been crucial in adapting to Chinese consumers' mobile-first preferences.
Partnerships with local e-commerce giants like Alibaba have been instrumental in enhancing Starbucks' online presence and delivery capabilities. The collaboration with Alibaba's Ele.me platform, for instance, has greatly expanded Starbucks' delivery reach.
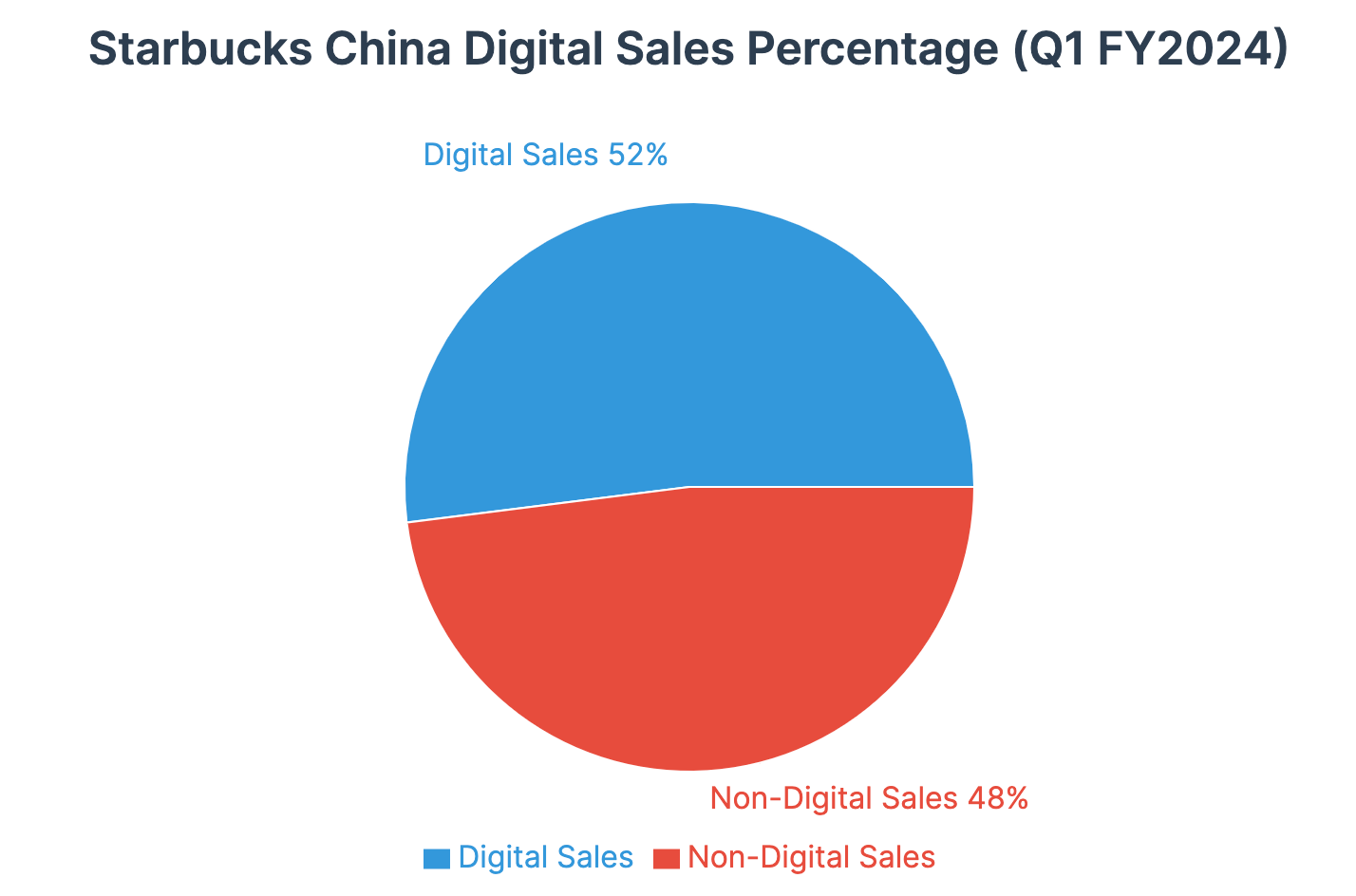
The company's digital transformation has shown promising results, with digital sales accounting for 52% of total sales in Q1 FY2024. However, this progress may be insufficient in a market where local competitors have built their entire business models around digital-first experiences.
Starbucks' Innovation and Technology Center (SITC) in Shenzhen, set to open in September 2023, represents a significant investment in accelerating the company's digital capabilities in China. The SITC's focus on data analytics, artificial intelligence, and new customer experiences could be crucial in helping Starbucks compete more effectively in the digital realm.
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape in China's coffee market has become increasingly fragmented and intense. While Starbucks remains a leading player with strong brand recognition, it faces mounting pressure from both local and international rivals.
Luckin Coffee has emerged as Starbucks' most formidable competitor in China. With over 13,000 stores, Luckin has surpassed Starbucks in terms of store count and has captured significant market share with its lower prices and focus on convenience and delivery.
Other international brands like Costa Coffee are also expanding their presence in China, adding to the competitive pressure. Additionally, a growing number of local specialty coffee chains and independent cafes are catering to niche markets and coffee enthusiasts, further fragmenting the market.
Starbucks has attempted to differentiate itself through its premium store experience and high-quality coffee offerings. However, as competitors improve their product quality and in-store experiences, this differentiation is becoming less pronounced.
The company's ability to navigate this intensely competitive landscape will be crucial for its future success in China. This may require a reassessment of its premium positioning and a more aggressive approach to digital innovation and localization.
Future Growth Prospects
Despite the challenges, Starbucks' growth prospects in China remain significant. The company's established brand, extensive store network, and loyal customer base provide a strong foundation for future growth.
Continued expansion into lower-tier cities presents an opportunity for Starbucks to tap into new markets. However, this expansion must be balanced with the need to maintain profitability and avoid market saturation.
Starbucks' ongoing investments in digital capabilities and sustainability initiatives could drive future growth by enhancing customer engagement and brand loyalty. The success of these efforts will depend on the company's ability to execute effectively and stay ahead of rapidly evolving consumer preferences.
The recent leadership change at Starbucks suggests that the company may be preparing for a strategic shift. The new CEO's approach to the Chinese market will be crucial in determining Starbucks' future growth trajectory in this key market.
Checking the Scale
Dark Side
Starbucks faces several significant challenges in China, including:
- Intense competition from local players like Luckin Coffee
- Increasing price sensitivity among consumers
- The need to accelerate digital transformation
- Balancing expansion with profitability
- Adapting to rapidly changing consumer preferences
- Potential regulatory risks as a prominent foreign brand
Bright Side
However, these challenges are balanced by several opportunities:
- Growing demand for premium coffee experiences
- Increasing adoption of digital payment and delivery services
- Expansion potential in lower-tier cities
- Rising interest in sustainability and ethical consumption
- Opportunities for product innovation tailored to local tastes
Starbucks' success in China will depend on its ability to effectively navigate these challenges while capitalizing on the opportunities presented by this dynamic market.
Conclusion
Starbucks' China strategy has been a cornerstone of its global growth plans, but recent developments suggest that the company is at a critical juncture. The unexpected leadership change, coupled with intensifying competition and evolving consumer preferences, calls for a comprehensive reassessment of Starbucks' approach to the Chinese market.
While Starbucks has built a strong brand and extensive store network in China, its premium positioning and expansion strategy may need adjustment to address the realities of a more competitive and price-sensitive market. The company's digital transformation efforts, while promising, must accelerate to keep pace with digitally-native competitors.
The success of Starbucks in China will hinge on its ability to balance its global brand identity with authentic localization, accelerate digital innovation, and potentially reevaluate its pricing strategy. The new leadership will face the challenge of crafting a strategy that maintains Starbucks' premium brand image while addressing the need for greater accessibility and value in a highly competitive market.
As Starbucks navigates this pivotal period, its ability to adapt and evolve will determine whether it can regain momentum and secure long-term success in the world's most populous market. The company's performance in China will not only shape its future in Asia but will likely have significant implications for its global growth strategy and financial performance in the years to come.





