In an era of rapid technological advancement and shifting economic landscapes, Mastercard (MA) finds itself at the intersection of two significant transitions: a substantial workforce reduction and the phasing out of the iconic magnetic stripe technology. These developments mark a pivotal moment for the global payments giant, reflecting broader trends in the financial technology sector and setting the stage for the future of payment systems worldwide.
The Changing Face of Mastercard's Workforce
Mastercard's recent announcement of a new layoff program has sent ripples through the financial technology industry. The company plans to reduce its global workforce by approximately 8%, affecting around 2,800 employees out of its 35,000-strong team. This move, slated to unfold throughout 2024, is part of Mastercard's strategy to realign its workforce with evolving strategic priorities.
The decision to implement these layoffs stems from Mastercard's need to optimize resources and sharpen its focus on high-growth areas such as digital payments and cybersecurity. As the payments landscape continues to evolve at a breakneck pace, companies like Mastercard must adapt swiftly to maintain their competitive edge. This restructuring effort, while challenging for affected employees, is aimed at improving operational efficiency and positioning the company for future success in an increasingly digital-first world.
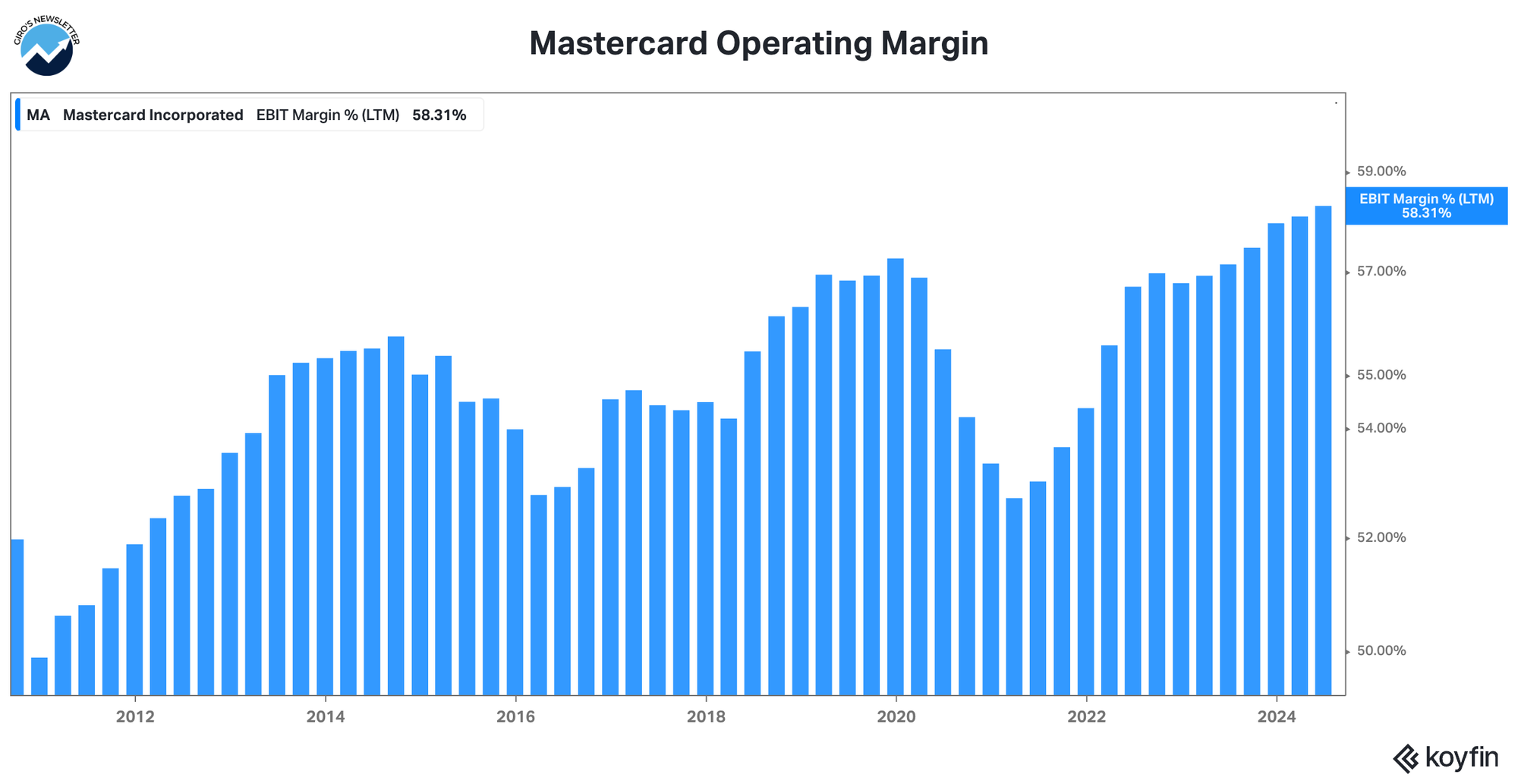
Mastercard is a 58% EBIT Margin company that benefits from rising inflation. Obviously, the company has to present a formal reason for the new layoff program, although this one was laughable.
The Twilight of Magnetic Stripes: A Technological Shift
Parallel to its workforce changes, Mastercard is leading the charge in phasing out magnetic stripe technology on payment cards. This transition (finally!) marks the end of an era for a feature that has been ubiquitous on credit and debit cards for decades. Mastercard's timeline for this phase-out is both ambitious and measured, reflecting the complex nature of global payment systems.
Starting in 2024, newly-issued Mastercard credit and debit cards will no longer be required to have magnetic stripes in most markets, particularly in regions where chip cards are already widely used, such as Europe. The company has outlined a gradual phase-out plan, with key milestones including the removal of the magnetic stripe requirement for banks in the United States by 2027 and the complete elimination of magnetic stripes on all Mastercard credit and debit cards by 2033.
This transition is driven by several factors, including enhanced security features of newer technologies, changing consumer preferences, and the need to reduce fraud. Chip-based and contactless payment methods offer significantly improved security through features like unique transaction codes and tokenization, making them far more resistant to skimming and counterfeiting compared to magnetic stripes.
A Symbolic Shift

Mastercard's announcement to phase out magnetic stripe technology on payment cards by 2033 is more symbolic than transformative. This decision reflects the culmination of a long-term shift in payment technologies that has been underway for years. In reality, the use of magnetic stripes has already declined significantly, with chip-based and contactless payments becoming the norm in most markets.
The timeline for this phase-out is notably extended, with the process beginning in 2024 and concluding in 2033. This prolonged timeline isn't indicative of major challenges in transitioning away from magnetic stripes, but rather an acknowledgment that the shift has already largely occurred organically.
Current State of Payment Technologies
In today's payment landscape, chip-based cards and contactless payments dominate transactions in most developed markets. The shift away from magnetic stripes has been gradual and largely seamless for both consumers and merchants. This transition has been driven by several factors:
Enhanced Security: EMV chip technology, which generates unique codes for each transaction, has significantly reduced fraud compared to magnetic stripes.
Convenience: Contactless payments, using both cards and mobile devices, offer faster transaction times and improved user experience.
Regulatory Push: Many countries have implemented regulations favoring chip-based cards, accelerating the move away from magnetic stripes.
Consumer Preference: As consumers have become more comfortable with digital and contactless payment methods, the demand for magnetic stripe use has naturally declined.
Global Adoption of Modern Payment Methods
The adoption of newer payment technologies varies globally, but the trend is clear:
In the United Kingdom, there were over 142 million contactless-enabled cards in circulation as of October 2021.
Australia has seen contactless transactions account for 4 out of 5 point-of-sale credit card purchases as early as 2019.
In the United States, which had been slower to adopt new payment methods, Visa estimated 300 million contactless cards would be issued by the end of 2020.
Emerging markets have seen rapid adoption of digital payment methods, often leapfrogging traditional card technologies altogether. For instance, in Latin America, the share of individuals using digital payments increased from 10% in 2014 to 28% in 2021 among the poorest quintile.
The Future of Payments
As magnetic stripes fade into obsolescence, the payment industry continues to evolve. Current and emerging technologies shaping the future of transactions include:
Biometric Authentication: Incorporating fingerprint or facial recognition for enhanced security.
Tokenization: Replacing sensitive data with unique identification symbols to protect transaction information.
Internet of Things (IoT) Payments: Enabling seamless transactions through connected devices.
Blockchain and Cryptocurrencies: Exploring decentralized payment systems and digital currencies.
Artificial Intelligence: Enhancing fraud detection and personalizing payment experiences.
These technologies are not replacing magnetic stripes directly, but rather building upon the digital payment ecosystem that has been developing for years.
Mastercard's decision to phase out magnetic stripes is less about driving a new change and more about formally recognizing the evolution that has already taken place in the payments industry. It underscores the company's commitment to aligning with current payment practices and sets the stage for future innovations in the rapidly evolving world of financial technology.
Frequently Asked Questions
When will Mastercard completely phase out magnetic stripes?
Mastercard plans to complete the phase-out of magnetic stripes by 2033. However, the process will begin much earlier, with newly-issued cards in most markets not requiring magnetic stripes starting from 2024.
How will the layoffs affect Mastercard's operations?
Mastercard expects the layoffs to improve operational efficiency. The company aims to realign its workforce with strategic priorities, focusing on high-growth areas like digital payments and cybersecurity.
What are the main advantages of newer payment technologies over magnetic stripes?
Newer technologies like EMV chips and contactless payments offer enhanced security through unique transaction codes and tokenization. They also provide faster transaction times and additional features that magnetic stripes cannot support.
How can small businesses prepare for the transition away from magnetic stripe technology?
Small businesses should start planning for the upgrade of their payment systems to accept chip and contactless payments. They may want to consider solutions like Cloud Tap on Phone technology, which can turn smartphones into payment acceptance devices without additional hardware.
Will consumers need to replace their Mastercard before 2033 if it has a magnetic stripe?
While Mastercard plans to phase out magnetic stripes by 2033, consumers will likely receive updated cards from their issuing banks well before this deadline as part of regular card replacement cycles. However, it's best to check with your specific bank for their timeline on transitioning to stripe-less cards.




