Earnings Per Share (EPS) is a crucial financial metric that tells investors about a company’s profitability on a per-share basis. It’s calculated by dividing a company’s net income by its number of outstanding shares. This simple yet powerful ratio provides valuable insights into a company’s financial health and performance, although it should be considered alongside other indicators to get a complete picture of the company's financial health.
The Importance of EPS in Financial Analysis
Company's earnings serve as a key indicator of a company’s ability to generate profits for its shareholders. It’s widely used by analysts, investors, and financial professionals to assess corporate value and make investment decisions. Understanding how to analyze EPS trends is essential for anyone looking to evaluate a company’s financial performance and potential stock value.
Before you dive into our in-depth analysis, we have a quick request:
If you find this content useful, please consider sharing it!
Why? Your shares help us reach a wider audience, allowing us to continue producing high-quality, comprehensive content like this—completely free, with no paywalls or subscriptions.
Thank you for your support!
Basic EPS vs. Diluted EPS: Key Differences
When analyzing EPS, it’s important to distinguish between two types:
- Basic EPS: Calculated using the current number of outstanding shares.
- Diluted EPS: Accounts for all potential dilution from convertible securities and stock options, providing a comprehensive view of a company's diluted EPS.
Diluted EPS is often considered a more conservative and accurate measure, as it provides a worst-case scenario of earnings power on a per-share basis.
The EPS Calculation: Breaking Down the Formula
To effectively analyze EPS trends, you must first understand how to calculate earnings and how EPS is calculated. The basic formula for EPS is:
EPS = (Net Income - Preferred Dividends) / Outstanding Shares
Let’s break this down further:
- Net Income: The company’s total earnings or profit for a given period.
- Preferred Dividends: Payments made to preferred stockholders.
- Outstanding Shares: The total number of shares currently held by all shareholders.

Why We Subtract Preferred Dividends
It's crucial to subtract preferred dividends when calculating EPS because these payments represent earnings that are not available to common stockholders. This adjustment ensures that the EPS figure accurately reflects the earnings available to owners of common stock.

Practical Application: Calculating EPS from Financial Statements
To calculate EPS using a company’s financial statements:
- Find the company’s net income on the income statement. The company's net income is the profit after taxes and preferred dividends, which is crucial for assessing profitability on a per-share basis.
- Locate any preferred dividends in the equity section of the balance sheet or the statement of shareholders’ equity.
- Determine the number of outstanding shares from the balance sheet or the company’s latest SEC filings.
- Apply the EPS formula using these figures.
Example: If a company reports a net income of $10 million, pays $1 million in preferred dividends, and has 5 million outstanding shares, the EPS would be:
EPS = ($10,000,000 - $1,000,000) / 5,000,000 = $1.80
The Relationship Between EPS and Stock Value: A Critical Analysis
Understanding how EPS trends impact the company's share price and stock value is crucial for investors. Generally, a higher EPS is considered better, as it indicates that a company is more profitable and has more earnings to distribute to shareholders.
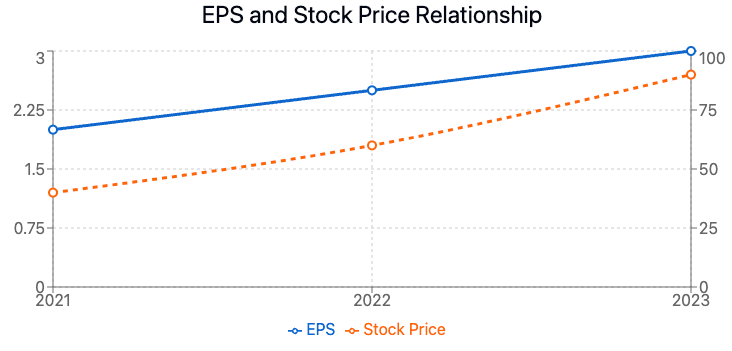
How EPS Growth Impact Investor Confidence
EPS growth rates are a key factor in shaping investor sentiment. A consistently increasing EPS often leads to higher investor confidence and can drive up a company's stock price. Conversely, declining EPS growth may signal potential issues and lead to decreased investor confidence.
The Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio: Connecting EPS to Stock Price
The P/E ratio, calculated by dividing a company's stock price by its EPS, provides valuable context for EPS analysis. A high P/E ratio might indicate that investors expect high earnings growth in the future, while a low P/E ratio could suggest that the company is undervalued or that investors have low expectations for future growth.

Navigating the Limitations: Key Considerations in EPS Analysis
While EPS is a powerful tool for financial analysis, it's not without limitations. Understanding these constraints is crucial for developing a comprehensive approach to analyzing EPS trends.
Potential for EPS Manipulation: What Investors Should Watch For
Companies may sometimes attempt to manipulate their EPS figures to present a more favorable picture of their financial health. Some tactics to be aware of include:
- Share Buybacks: Reducing the number of outstanding shares can artificially inflate EPS.
- Accounting Techniques: One-time charges or gains can distort EPS figures.
- Timing of Revenue Recognition: Companies may accelerate or delay revenue recognition to manage EPS.
Beyond EPS: Complementary Metrics for Net Income Comprehensive Analysis
To gain a holistic view of a company's financial health, consider these additional metrics alongside EPS:
- Return on Equity (ROE): Measures how efficiently a company uses shareholder equity to generate profits.
- Free Cash Flow (FCF): Indicates the cash a company generates after accounting for capital expenditures.
- Debt-to-Equity Ratio: Assesses a company's financial leverage.

Mastering EPS Analysis During Earnings Seasons
Earnings seasons provide crucial windows for analyzing EPS trends and their impact on stock value. These quarterly periods, when publicly traded companies release their financial results, offer investors rich opportunities to assess EPS performance in context.
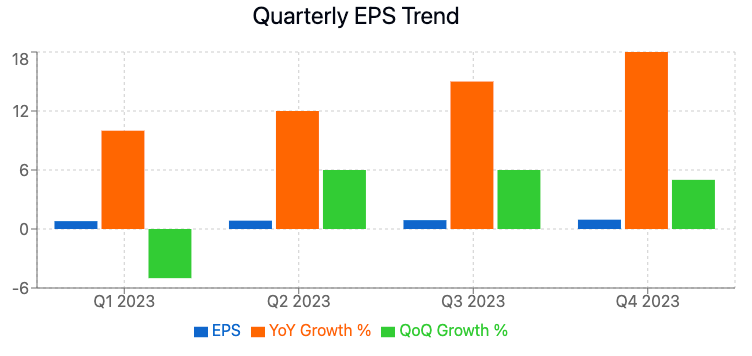
Interpreting Quarterly EPS Reports: Beyond the Headlines
When a company releases its quarterly earnings report, look beyond the headline EPS figure:
- Compare to Analyst Estimates: Understand how the reported EPS compares to market expectations.
- Analyze Year-over-Year (YoY) and Sequential Growth: Compare EPS to the same quarter last year and the previous quarter.
- Examine EPS Guidance: Pay attention to management's forward-looking EPS projections.
Factors Influencing EPS During Reporting Periods
Several factors can impact a company’s EPS during a given quarter:
- Revenue Changes: Increased sales can boost EPS if expenses remain controlled.
- Expense Management: Effective cost control can improve EPS even in challenging revenue environments.
- Share Count Fluctuations: Stock buybacks or issuances can significantly impact EPS calculations by altering the number of shares outstanding.
The Impact of EPS on Dividend Payments: A Crucial Connection
For income-focused investors, understanding the relationship between EPS trends and dividend payments is essential. EPS serves as a key indicator of a company's profitability and its ability to maintain and grow its dividend distributions.
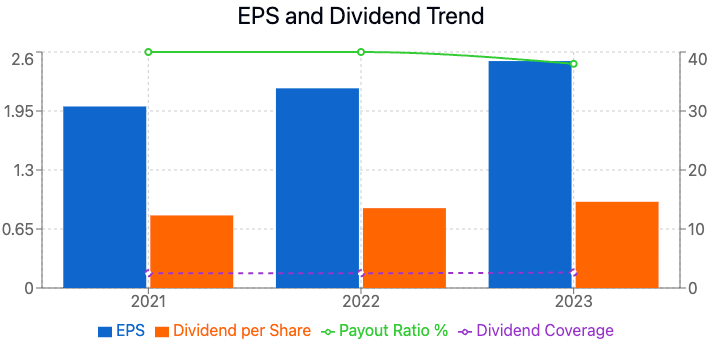
How EPS Growth Influences Dividend Policies
- Dividend Sustainability: A consistently growing EPS provides a solid foundation for sustainable dividend payments.
- Dividend Growth Potential: Strong EPS growth often leads to dividend increases.
- Payout Ratio Considerations: A lower payout ratio coupled with high EPS growth can signal potential for future dividend increases.
Analyzing the EPS-Dividend Relationship: Key Metrics
When evaluating how EPS trends impact dividend payments, consider these metrics:
- Payout Ratio: (Dividends per Share / EPS) x 100
- Dividend Coverage Ratio: EPS / Dividends per Share
- Dividend Growth Rate vs. EPS Growth Rate
Frequently Asked Questions
What does EPS growth rate tell you?
The EPS growth rate indicates how quickly a company is increasing its profitability on a per-share basis. A high EPS growth rate suggests that the company is effectively growing its earnings relative to its number of outstanding shares.
What happens when EPS increases?
When EPS increases, it generally indicates that a company's profitability is improving. This can lead to increased investor confidence, potentially driving up the company's stock price. Higher EPS may also support dividend growth for companies that pay dividends.
Is high EPS growth good?
Generally, high EPS growth is considered positive as it indicates improving profitability. However, it's important to consider the sustainability of this growth and compare it to industry averages. Extremely high growth rates may not be sustainable in the long term.
What are the benefits of increasing EPS?
Increasing EPS can lead to:
- Higher stock prices
- Increased investor confidence
- Greater ability to pay dividends
- Improved access to capital
- Enhanced company valuation
What is a good EPS trend?
A good EPS trend typically shows consistent growth over time. This indicates that the company is steadily increasing its profitability. However, the definition of "good" can vary by industry and company size.
Is a higher or lower EPS better?
Generally, a higher EPS is better as it indicates greater profitability per share. However, it's important to compare EPS figures within the same industry and consider other financial metrics for a comprehensive analysis.
Why is EPS significant?
EPS is significant because it:
- Provides a standardized measure of profitability
- Allows for easy comparison between companies
- Is a key component in valuation metrics like the P/E ratio
- Influences investor decisions and stock prices
- Helps in assessing dividend sustainability
Where can I find historical EPS data?
Historical EPS data can be found in:
- Company annual reports and SEC filings
- Financial websites like Yahoo Finance or Google Finance
- Paid financial databases such as Bloomberg or FactSet
- Brokerage research reports
What are the ways to calculate EPS?
There are several ways to calculate EPS:
- Basic EPS: (Net Income - Preferred Dividends) / Outstanding Shares
- Diluted EPS: Adjusts for potential dilution from convertible securities
- Trailing EPS: Uses data from the past 12 months
- Forward EPS: Based on analysts' earnings projections
How do you analyze EPS?
To analyze EPS effectively:
- Compare EPS trends over multiple periods
- Evaluate EPS growth rates
- Compare EPS to industry peers
- Consider both basic and diluted EPS
- Analyze EPS in conjunction with other financial metrics
- Examine factors influencing EPS changes
The Enduring Importance of EPS in Investment Analysis
Mastering the art and science of EPS trend analysis is crucial for making informed investment decisions. While EPS is a powerful tool, it's most effective when used as part of a comprehensive analysis that considers multiple financial metrics, industry trends, and broader economic factors.
By staying informed, adapting to new analytical methods, and maintaining a balanced perspective, investors can leverage EPS trends to gain valuable insights into a company's financial health, profitability, and potential for future growth. Remember, while a high EPS or strong EPS growth is generally positive, it's essential to consider the broader context and use EPS as one of many tools in your investment analysis toolkit.





