In the dynamic world of Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) and commercial real estate investing, understanding key financial metrics is crucial for making informed decisions. One metric that stands out as particularly important is Net Operating Income (NOI). This comprehensive guide will walk you through the ins and outs of NOI, its calculation, importance, and how to leverage it for better investment outcomes in the REIT sector.
What is Net Operating Income (NOI) in Real Estate?
Net Operating Income, commonly abbreviated as NOI, is a fundamental financial metric used extensively in the real estate industry, particularly for evaluating the performance of income-generating properties and REITs. It's a measure that provides crucial insight into a property's ability to generate income after accounting for all necessary operating expenses.
Definition and Importance of Net Operating Income (NOI)
Net Operating Income (NOI) is defined as the total revenue generated by a property minus all reasonably necessary operating expenses. This metric is crucial because it:
- Provides a clear picture of a property's profitability
- Helps real estate investors compare different properties or REITs
- Is used in various other calculations, such as capitalization rate (cap rate)
- Influences property valuation and lending decisions by commercial lenders
For REIT investors, understanding net operating income is particularly important as it directly impacts the REIT's overall performance and, consequently, potential returns for shareholders. The property's net operating income serves as a key indicator of its financial health and income generation potential.
NOI vs. Other Financial Metrics
It's essential to distinguish net operating income (NOI) from other financial metrics commonly used in real estate and finance:
- Gross Operating Income (GOI): This is the total income generated before subtracting operating expenses. While GOI gives an indication of a property's revenue-generating potential, it doesn't account for the costs associated with running the property.
- Net Income: Unlike NOI, net income includes non-operating expenses like debt service (principal and interest payments) and is calculated after income taxes. For real estate investors, net income provides a bottom-line figure but doesn't isolate the property's operational performance.
- EBITDA (Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization): While similar to NOI, EBITDA is used more broadly across industries and includes non-property related income and expenses. In real estate, NOI is generally preferred as it focuses specifically on property-level performance.
- Cash Flow: This metric includes all cash inflows and outflows, including those related to financing activities. While cash flow is important for understanding a property's overall financial position, NOI provides a clearer picture of operational performance.
Understanding these distinctions is crucial for real estate investors and industry professionals when analyzing properties or REITs.
Calculating Net Operating Income: A Step-by-Step Approach
Understanding how to calculate net operating income is crucial for any REIT investor or real estate professional. Let's break down the process step-by-step, using the net operating income formula.
Step 1: Determine Gross Operating Income (GOI)
Start by calculating the Gross Operating Income. For a REIT, this typically includes:
- Rental income from properties
- Additional income sources (e.g., parking fees, vending machines, laundry facilities)
For example, let's consider a hypothetical REIT, "UrbanCore REIT," which owns a mix of office and retail properties:
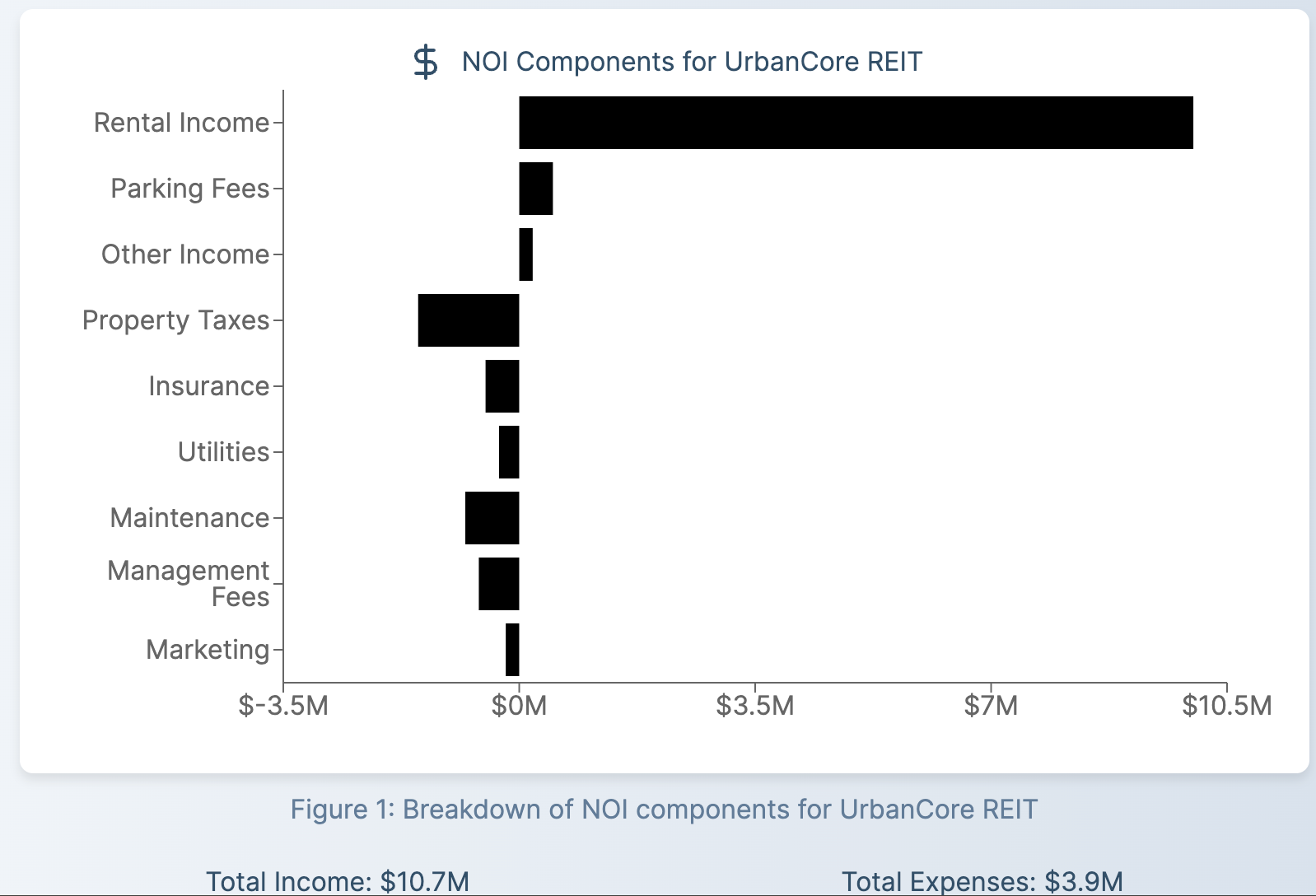
Total Gross Operating Income: $10,700,000
It's important to note that when calculating gross operating income, you should consider potential rental income, accounting for vacancy and credit losses. This gives a more accurate picture of the property's income-generating capacity.
Step 2: Calculate Operating Expenses
Next, sum up all the operating expenses. These typically include:
- Property taxes
- Insurance
- Utilities (if not paid by tenants)
- Maintenance costs and repairs
- Property management fees
- Marketing and advertising costs
Continuing with our UrbanCore REIT example:
| Expense Category | Amount |
|---|---|
| Property Taxes | $1,500,000 |
| Insurance | $500,000 |
| Utilities | $300,000 |
| Maintenance | $800,000 |
| Management Fees | $600,000 |
| Marketing | $200,000 |
Total Operating Expenses: $3,900,000
It's crucial to note that operating expenses do not include capital expenditures, principal and interest payments, income taxes, or depreciation. These are considered separately in other financial analyses.
Step 3: Apply the Net Operating Income Formula
Now, we can apply the NOI formula:
NOI = Gross Operating Income - Operating Expenses
For UrbanCore REIT:
NOI = $10,700,000 - $3,900,000 = $6,800,000
This means that after accounting for all operating expenses, UrbanCore REIT generates $6.8 million in net operating income.
Understanding the NOI Calculation
The NOI calculation provides valuable insights into a property's or REIT's operational efficiency. Here are some key points to remember:
- NOI focuses solely on operating income and expenses, excluding factors like financing costs, capital expenditures, and income taxes.
- It represents the income generated by the property before accounting for any debt service or income tax obligations.
- NOI can be used to calculate other important metrics like the capitalization rate (cap rate) and debt service coverage ratio.
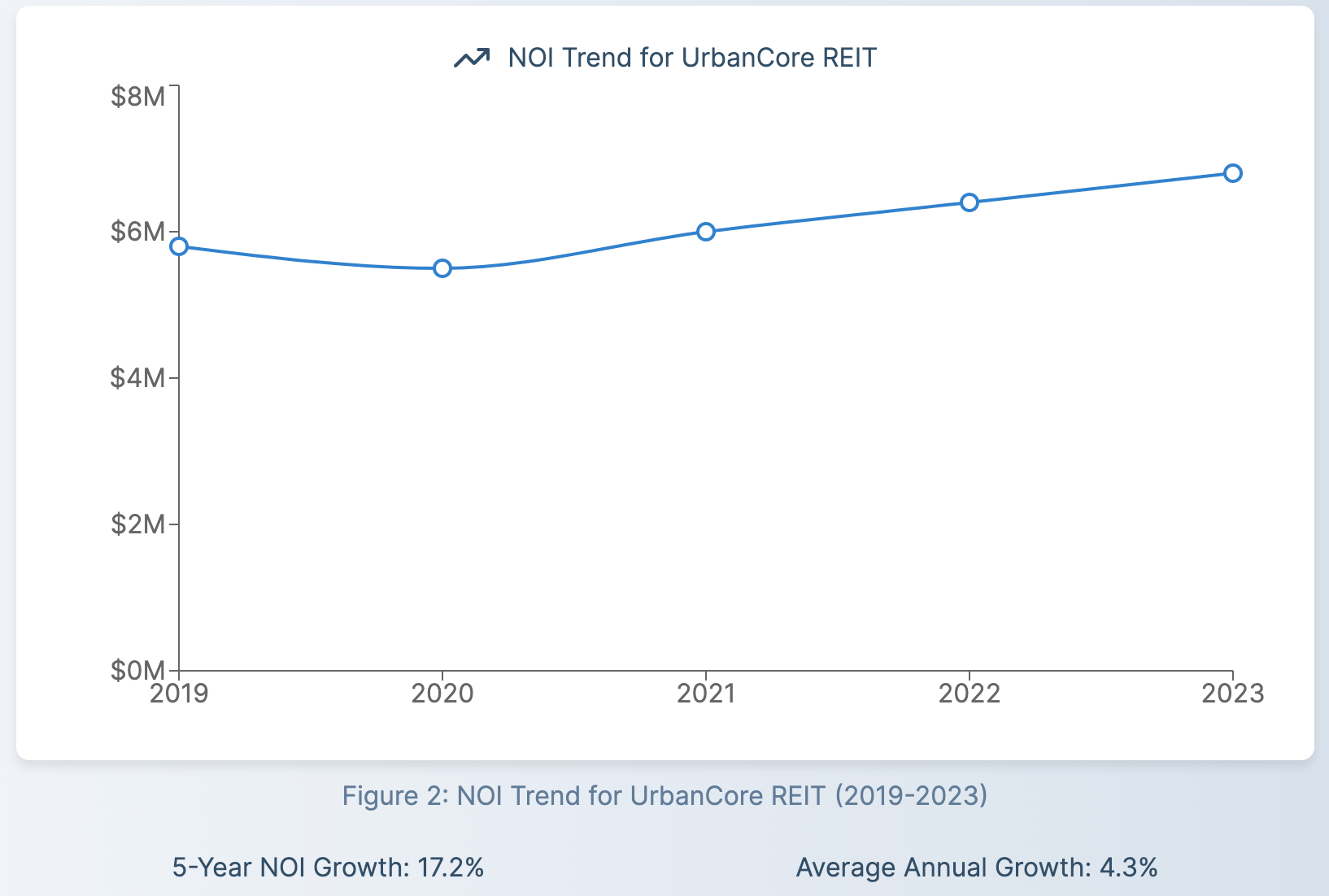
Factors Affecting Net Operating Income in REITs
Several factors can impact a REIT's NOI, and understanding these can help investors make more informed decisions:
1. Occupancy Rates
Higher occupancy rates generally lead to increased rental income, positively affecting NOI. Conversely, high vacancy rates can significantly reduce NOI. Real estate investors should pay close attention to a REIT's ability to maintain high occupancy levels across its portfolio.
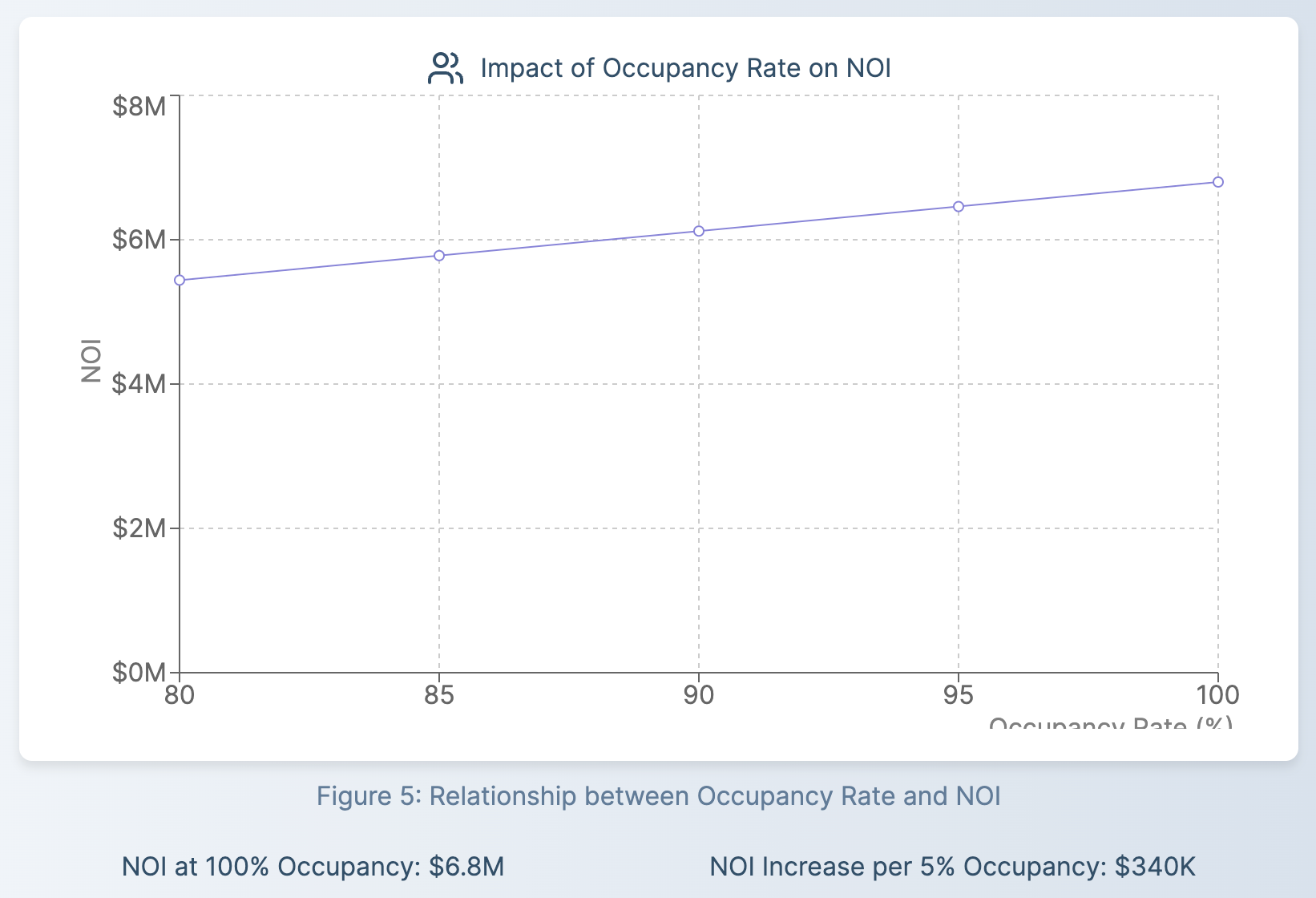
2. Rental Rates
The ability to charge competitive rental rates while maintaining high occupancy is crucial. Market conditions, property quality, and location all play a role in determining achievable rental rates. A REIT's management team should strive to optimize rental income without sacrificing occupancy.
3. Operating Expense Management
Efficient management of operating expenses can significantly impact NOI. This includes:
- Implementing energy-efficient systems to reduce utility costs
- Negotiating favorable contracts with service providers
- Proactive maintenance to prevent costly repairs
Property management plays a crucial role in controlling these expenses and maximizing NOI.
4. Market Conditions
Economic factors, such as local job growth, population trends, and overall market demand, can affect both income potential and operating costs. Real estate investors should consider the broader market context when evaluating a REIT's NOI performance.
5. Property Type and Quality
Different property types (e.g., office buildings, retail spaces, residential complexes) may have varying income potentials and expense structures. Additionally, higher-quality properties might command premium rents but may also incur higher maintenance costs. Understanding the composition of a REIT's portfolio is crucial for interpreting its NOI figures.
Using NOI to Evaluate REIT Performance
For REIT investors, NOI serves as a crucial tool for assessing the performance and potential of different investment opportunities. Here's how you can leverage NOI in your investment analysis:
1. Comparing REITs
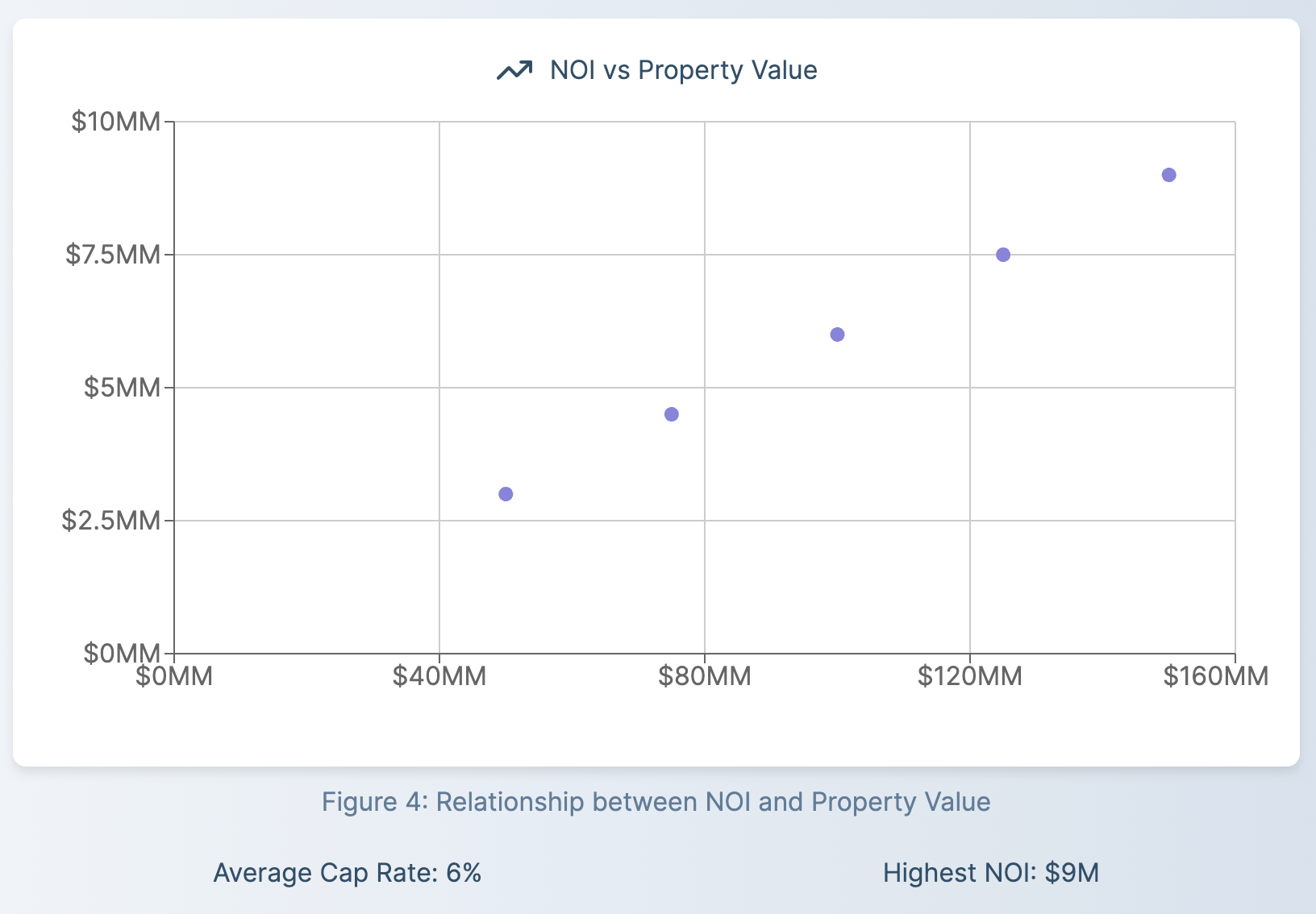
NOI allows for a more accurate comparison between different REITs, even if they have different capital structures or tax situations. A higher NOI generally indicates better operational efficiency. However, it's important to consider NOI in relation to the total value of the properties or the REIT's market capitalization.
2. Assessing Management Effectiveness
By tracking a REIT's NOI over time, investors can gauge how effectively the management team is operating the properties and growing income. Consistent NOI growth can be a sign of strong management and a profitable investment opportunity.
3. Calculating Key Ratios
NOI is used in calculating important real estate metrics, such as:
- Capitalization Rate (Cap Rate) = NOI / Property Value
- Debt Service Coverage Ratio (DSCR) = NOI / Total Debt Service
These ratios provide additional insights into a REIT's financial health and risk profile.
4. Projecting Future Performance
Analyzing trends in NOI can help investors project a REIT's future performance and potential for dividend growth. However, it's important to consider other factors like market conditions and the REIT's growth strategy when making these projections.
Best Practices to Increase Net Operating Income
For REIT managers (and for investors to look out for), there are several strategies to improve NOI:
- Optimize Rental Income: Implement strategic rent increases where market conditions allow. This can directly boost the gross operating income.
- Reduce Vacancy: Enhance marketing efforts and improve tenant retention strategies to minimize vacancy and credit losses.
- Minimize Operating Expenses: Implement energy-efficient systems, negotiate better contracts with service providers, and conduct regular preventative maintenance.
- Explore Additional Income Sources: Consider adding amenities or services that can generate extra income (e.g., premium parking, storage spaces).
- Invest in Property Improvements: Strategic upgrades can justify higher rents and attract higher-quality tenants, potentially increasing both rental income and property value.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Analyzing NOI
When evaluating REITs based on NOI, be wary of these common pitfalls:
- Ignoring Capital Expenditures: While not included in NOI calculations, significant capital expenditures can impact a REIT's overall profitability and should be considered in your broader analysis.
- Overlooking Market Context: A high NOI doesn't always indicate a good investment if the property is in a declining market. Consider the broader economic and real estate market trends.
- Failing to Consider Seasonality: Some properties may have seasonal fluctuations in income or expenses that can skew NOI if not properly accounted for.
- Not Adjusting for One-Time Items: Unusual or one-time income or expenses should be normalized when using NOI for long-term projections.
- Neglecting Property-Specific Factors: Different property types and locations can have vastly different NOI profiles. Make sure to consider these factors when comparing NOIs across different properties or REITs.
Conclusion: Mastering NOI for Smarter REIT Investments
Net Operating Income is more than just a financial metric—it's a powerful tool that provides deep insights into the operational efficiency and income-generating potential of real estate investments. For REIT investors, mastering the concept of NOI and its implications can lead to more informed investment decisions and potentially better returns.
By understanding how to calculate NOI, the factors that influence it, and how to use it in conjunction with other metrics, you'll be better equipped to:
- Evaluate the performance of different REITs
- Assess the effectiveness of REIT management teams
- Make more accurate projections about future REIT performance
- Identify REITs with the potential for growth and value appreciation
Remember, while NOI is a crucial metric, it should be used as part of a comprehensive investment analysis strategy. Consider other factors such as market trends, the REIT's growth strategy, and broader economic conditions when making investment decisions.
As you continue to invest in REITs, let NOI be your guide to uncovering value and potential in the dynamic world of real estate investment trusts. By consistently applying the principles and insights discussed in this guide, you'll be well-positioned to make more informed and potentially more profitable investment decisions in the REIT market.
Frequently Asked Questions About Net Operating Income in REITs
How do you calculate net operating income?
To calculate net operating income (NOI), follow these steps:
- Determine the Gross Operating Income (GOI) by summing all revenue sources.
- Calculate total operating expenses, including property taxes, insurance, maintenance, and management fees.
- Apply the NOI formula: NOI = Gross Operating Income - Operating Expenses
This calculation provides a clear picture of a property's income-generating ability after accounting for essential operating costs.
Is net operating income the same as profit?
No, net operating income is not the same as profit. While NOI represents the income generated by a property after operating expenses, it does not account for costs such as income taxes, interest payments, capital expenditures, or depreciation. Profit, or net income, includes these additional expenses. NOI is specifically focused on operational performance, while profit provides a more comprehensive view of overall financial performance.
What is actual net operating income?
Actual net operating income refers to the NOI calculated using real, historical financial data rather than projected or pro forma figures. It represents the true operational performance of a property or REIT over a specific period, typically a year. Actual NOI is crucial for investors as it provides a factual basis for analyzing a property's or REIT's performance and can be used to assess the accuracy of previous projections.
What is a good NOI?
Determining a "good" NOI depends on various factors, including property type, location, and market conditions. Generally, a higher NOI indicates better operational efficiency and profitability. However, it's more meaningful to evaluate NOI in context:
- Compare the NOI to the property's value or purchase price (this is the capitalization rate or cap rate).
- Assess the NOI trend over time – consistent growth is typically a positive sign.
- Compare the NOI to similar properties or REITs in the same market.
- Consider the NOI in relation to the property's age, condition, and potential for future value appreciation.
A "good" NOI should provide sufficient income to cover debt service (if any), allow for necessary capital expenditures, and provide an attractive return to investors. The specific threshold for a "good" NOI will vary based on investment goals and market conditions.




