In today's digital landscape, understanding how to effectively value data has become crucial for businesses seeking to make informed decisions and develop winning strategies. This comprehensive guide explores the intricacies of data valuation, offering insights into methodologies, best practices, and the impact of data quality on business success.
Understanding Data as an Asset
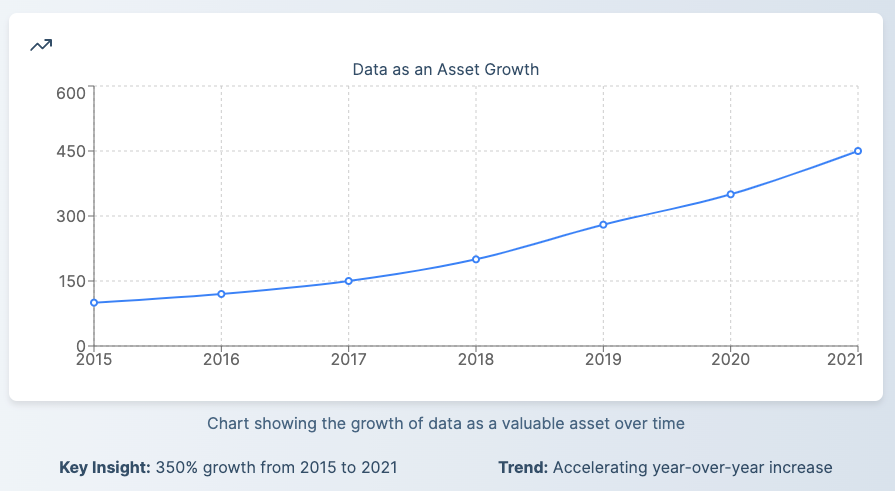
The concept of data as an asset has revolutionized investment approaches and business strategies. Data valuation, the process of determining the monetary value or intrinsic value of data, has become increasingly important in our data-driven world. Companies that effectively leverage their data assets can gain a significant competitive advantage and create innovative business models.
Data assets can be used to gain market insights, improve decision-making processes, enhance product development, optimize operations, and create new revenue streams. For instance, a retail company might use customer data to create a highly effective personalized recommendation system, significantly boosting sales and customer loyalty. This exemplifies how data valuation enables businesses to unlock hidden potential within their existing data. Data owners play a crucial role in leveraging data assets, as they must understand the worth of their data and navigate the complexities of measuring data utility and benefits.
Characteristics of Valuable Data and Valuation Methodologies
To accurately assess the value of data, it’s essential to understand the key characteristics that contribute to its worth. These factors play a crucial role in the data valuation process:
- Accuracy and Completeness: Data quality is paramount in determining the value of data. Accurate and complete data sets form the foundation for reliable analysis and decision-making.
- Relevance and Accessibility: Data that’s relevant to the business and easily accessible holds greater value. Organizations must ensure that their data management practices facilitate easy retrieval and analysis of pertinent information.
- Timeliness and Currency: The value of data often depends on its timeliness. Real-time or near-real-time data can be particularly valuable in certain contexts.
- Uniqueness and Scarcity: Data sets that are unique or difficult for competitors to replicate can be extremely valuable, providing a significant competitive advantage.
These characteristics contribute to the overall business value derived from data, emphasizing its importance in strategic data management and overall organizational value.
Several data valuation approaches have emerged to help organizations assess the worth of their data assets. The three main methodologies are:
- Cost Value Method: This method measures the cost to produce, store, and replace data, as well as the impact on cash flows if it was lost.
- Market Value Method: This approach tracks the current value of data based on what others pay for it in an active market or for comparable assets.
- Economic Value Method: This comprehensive method tracks the impact of data on the business’s bottom line, considering how data contributes to revenue generation, cost savings, and overall business performance.
Integrating these data valuation methodologies into business models is crucial to enhance stakeholder value and improve decision-making processes.
Building a Comprehensive Data Valuation Framework
To maximize the value of data assets, organizations should implement a robust data valuation framework encompassing data collection, data management, data quality assurance, data analysis and insights, and data monetization strategies.
Ensuring that the right data is being collected efficiently and ethically is the first step. Organizations must scrutinize their data collection practices, looking for comprehensive strategies that capture relevant information while respecting privacy concerns. Implementing robust systems to store, organize, and access data is crucial, as effective data management can dramatically increase the value and utility of data assets. Data-driven strategies are essential for modern businesses to adapt and thrive, facilitating better data management, monetization, and valuation, ultimately enabling organizations to create new business models and improve planning and forecasting.
Maintaining high standards for data accuracy and completeness is non-negotiable. Organizations should implement rigorous data quality processes, including regular audits and cleaning procedures. The ability to extract meaningful insights from data is where much of its value lies, so investing in strong data analysis capabilities is essential.
Finally, exploring ways to generate revenue from data assets is the ultimate goal. This could involve using data to improve internal operations, enhance products or services, or even create new data-driven offerings.
Key Factors Impacting Data Value and Data Monetization Strategies
Several factors can significantly impact the value of data, including data security, data privacy compliance, data integration capabilities, scalability of data infrastructure, and data governance. A single data breach can destroy the value of data and lead to severe reputational and financial damage. Compliance with data protection regulations such as GDPR and CCPA has become crucial in data valuation.
The ability to integrate data from various sources can significantly enhance its value, often uncovering valuable insights that drive business growth. As data volumes grow, the ability to scale data infrastructure becomes crucial. Strong data governance practices ensure that data is managed as a valuable asset throughout its lifecycle, including clear policies on data ownership, usage, and quality control. The Business Model Maturity Index plays a crucial role in assessing the value of data in relation to specific business use cases, connecting data value to tangible business outcomes through detailed analysis.
Organizations can employ several strategies to generate revenue from their data assets:
- Data Licensing: Selling data to other businesses, particularly valuable for market research or product development.
- Data Analytics as a Service: Offering data analysis and interpretation services to other organizations.
- Data-Driven Product Enhancement: Using data to improve existing products or create new ones that address unmet customer needs.
- Data-Driven Advertising: Leveraging consumer data to deliver highly targeted advertising.
- Data Marketplaces: Facilitating the buying and selling of data between different parties.
The Importance of Data Quality and Common Challenges in Data Valuation
Data quality is critical when it comes to valuation. High-quality data – accurate, complete, and relevant – is the foundation of any successful data strategy. Poor data quality can lead to inaccurate valuations and, consequently, poor decision-making. Ensuring data quality involves regular data audits, implementing data validation processes, establishing clear quality standards, investing in data cleaning tools, and training employees on best practices.
Organizations often face several challenges when attempting to value their data assets, including complexity, lack of standardization, rapidly changing value, the intangible nature of data, and privacy and ethical concerns. Data valuation can be incredibly complex, especially when dealing with large, diverse datasets. The evolution and complexity of data valuation methodologies over time further complicate this process. Unlike financial transactions or tangible assets, there’s no standardized method for valuing data, making it difficult to compare data assets across different companies or industries.
The value of data can change rapidly based on market conditions, technological advancements, or regulatory changes. As an intangible asset, it can be challenging to separate the value of data from the value of the systems and people that collect, manage, and analyze it. Additionally, as data privacy regulations evolve, the ethical use of data has become a crucial consideration in valuation.
Best Practices for Data Valuation and Future Outlook
To effectively value data assets, organizations should adopt a holistic approach, using a combination of valuation methods to get a comprehensive view. Consider the broader data ecosystem and how data interacts with other assets, systems, and processes within the organization. Factor in future potential, anticipating how evolving technologies or market trends might unlock new value from existing data.
Regularly reassess the value of data assets, implement strong data governance practices, and invest in data literacy training for staff to maximize the potential of data assets. Balance the pursuit of data value with associated risks, including regulatory compliance, security risks, and potential reputational damage from misuse of data.
As we move forward in this data-driven world, the field of data valuation continues to evolve. New methodologies and best practices are likely to emerge in the coming years. The most successful companies will be those that not only accumulate vast amounts of data but also develop the capabilities to extract meaningful insights and act on them swiftly.
The future of data valuation looks promising, with artificial intelligence and machine learning enhancing our ability to derive value from data. These technologies promise to uncover patterns and insights that might be invisible to human analysts, potentially unlocking entirely new sources of value from existing data assets.
However, as we push the boundaries of data utilization, we must also be mindful of the ethical implications. Responsible data practices that respect privacy and promote transparency will be crucial for maintaining public trust and ensuring the long-term sustainability of data-driven business models.
In conclusion, the ability to accurately value and effectively leverage data assets will be a key differentiator in the business world of tomorrow. By staying curious, adaptable, and committed to ethical practices, organizations can navigate the complexities of data valuation and harness the full potential of the digital age. The future belongs to those who can see the value hidden in their data – and know how to unlock it.
In today's digital landscape, understanding how to effectively value data has become crucial for businesses seeking to make informed decisions and develop winning strategies. This comprehensive guide explores the intricacies of data valuation, offering insights into methodologies, best practices, and the impact of data quality on business success.
Understanding Data as an Asset
The concept of data as an asset has revolutionized investment approaches and business strategies. Data valuation, the process of determining the monetary value or intrinsic value of data, has become increasingly important in our data-driven world. Companies that effectively leverage their data assets can gain a significant competitive advantage and create innovative business models.
Data assets can be used to gain market insights, improve decision-making processes, enhance product development, optimize operations, and create new revenue streams. For instance, a retail company might use customer data to create a highly effective personalized recommendation system, significantly boosting sales and customer loyalty. This exemplifies how data valuation enables businesses to unlock hidden potential within their existing data. Data owners play a crucial role in leveraging data assets, as they must understand the worth of their data and navigate the complexities of measuring data utility and benefits.
Characteristics of Valuable Data and Valuation Methodologies
To accurately assess the value of data, it’s essential to understand the key characteristics that contribute to its worth. These factors play a crucial role in the data valuation process:
- Accuracy and Completeness: Data quality is paramount in determining the value of data. Accurate and complete data sets form the foundation for reliable analysis and decision-making.
- Relevance and Accessibility: Data that’s relevant to the business and easily accessible holds greater value. Organizations must ensure that their data management practices facilitate easy retrieval and analysis of pertinent information.
- Timeliness and Currency: The value of data often depends on its timeliness. Real-time or near-real-time data can be particularly valuable in certain contexts.
- Uniqueness and Scarcity: Data sets that are unique or difficult for competitors to replicate can be extremely valuable, providing a significant competitive advantage.
These characteristics contribute to the overall business value derived from data, emphasizing its importance in strategic data management and overall organizational value.
Several data valuation approaches have emerged to help organizations assess the worth of their data assets. The three main methodologies are:
- Cost Value Method: This method measures the cost to produce, store, and replace data, as well as the impact on cash flows if it was lost.
- Market Value Method: This approach tracks the current value of data based on what others pay for it in an active market or for comparable assets.
- Economic Value Method: This comprehensive method tracks the impact of data on the business’s bottom line, considering how data contributes to revenue generation, cost savings, and overall business performance.
Integrating these data valuation methodologies into business models is crucial to enhance stakeholder value and improve decision-making processes.
Building a Comprehensive Data Valuation Framework
To maximize the value of data assets, organizations should implement a robust data valuation framework encompassing data collection, data management, data quality assurance, data analysis and insights, and data monetization strategies.
Ensuring that the right data is being collected efficiently and ethically is the first step. Organizations must scrutinize their data collection practices, looking for comprehensive strategies that capture relevant information while respecting privacy concerns. Implementing robust systems to store, organize, and access data is crucial, as effective data management can dramatically increase the value and utility of data assets. Data-driven strategies are essential for modern businesses to adapt and thrive, facilitating better data management, monetization, and valuation, ultimately enabling organizations to create new business models and improve planning and forecasting.
Maintaining high standards for data accuracy and completeness is non-negotiable. Organizations should implement rigorous data quality processes, including regular audits and cleaning procedures. The ability to extract meaningful insights from data is where much of its value lies, so investing in strong data analysis capabilities is essential.
Finally, exploring ways to generate revenue from data assets is the ultimate goal. This could involve using data to improve internal operations, enhance products or services, or even create new data-driven offerings.
Key Factors Impacting Data Value and Data Monetization Strategies
Several factors can significantly impact the value of data, including data security, data privacy compliance, data integration capabilities, scalability of data infrastructure, and data governance. A single data breach can destroy the value of data and lead to severe reputational and financial damage. Compliance with data protection regulations such as GDPR and CCPA has become crucial in data valuation.
The ability to integrate data from various sources can significantly enhance its value, often uncovering valuable insights that drive business growth. As data volumes grow, the ability to scale data infrastructure becomes crucial. Strong data governance practices ensure that data is managed as a valuable asset throughout its lifecycle, including clear policies on data ownership, usage, and quality control. The Business Model Maturity Index plays a crucial role in assessing the value of data in relation to specific business use cases, connecting data value to tangible business outcomes through detailed analysis.
Organizations can employ several strategies to generate revenue from their data assets:
- Data Licensing: Selling data to other businesses, particularly valuable for market research or product development.
- Data Analytics as a Service: Offering data analysis and interpretation services to other organizations.
- Data-Driven Product Enhancement: Using data to improve existing products or create new ones that address unmet customer needs.
- Data-Driven Advertising: Leveraging consumer data to deliver highly targeted advertising.
- Data Marketplaces: Facilitating the buying and selling of data between different parties.
The Importance of Data Quality and Common Challenges in Data Valuation
Data quality is critical when it comes to valuation. High-quality data – accurate, complete, and relevant – is the foundation of any successful data strategy. Poor data quality can lead to inaccurate valuations and, consequently, poor decision-making. Ensuring data quality involves regular data audits, implementing data validation processes, establishing clear quality standards, investing in data cleaning tools, and training employees on best practices.
Organizations often face several challenges when attempting to value their data assets, including complexity, lack of standardization, rapidly changing value, the intangible nature of data, and privacy and ethical concerns. Data valuation can be incredibly complex, especially when dealing with large, diverse datasets. The evolution and complexity of data valuation methodologies over time further complicate this process. Unlike financial transactions or tangible assets, there’s no standardized method for valuing data, making it difficult to compare data assets across different companies or industries.
The value of data can change rapidly based on market conditions, technological advancements, or regulatory changes. As an intangible asset, it can be challenging to separate the value of data from the value of the systems and people that collect, manage, and analyze it. Additionally, as data privacy regulations evolve, the ethical use of data has become a crucial consideration in valuation.
Best Practices for Data Valuation and Future Outlook
To effectively value data assets, organizations should adopt a holistic approach, using a combination of valuation methods to get a comprehensive view. Consider the broader data ecosystem and how data interacts with other assets, systems, and processes within the organization. Factor in future potential, anticipating how evolving technologies or market trends might unlock new value from existing data.
Regularly reassess the value of data assets, implement strong data governance practices, and invest in data literacy training for staff to maximize the potential of data assets. Balance the pursuit of data value with associated risks, including regulatory compliance, security risks, and potential reputational damage from misuse of data.
As we move forward in this data-driven world, the field of data valuation continues to evolve. New methodologies and best practices are likely to emerge in the coming years. The most successful companies will be those that not only accumulate vast amounts of data but also develop the capabilities to extract meaningful insights and act on them swiftly.
The future of data valuation looks promising, with artificial intelligence and machine learning enhancing our ability to derive value from data. These technologies promise to uncover patterns and insights that might be invisible to human analysts, potentially unlocking entirely new sources of value from existing data assets.
However, as we push the boundaries of data utilization, we must also be mindful of the ethical implications. Responsible data practices that respect privacy and promote transparency will be crucial for maintaining public trust and ensuring the long-term sustainability of data-driven business models.
In conclusion, the ability to accurately value and effectively leverage data assets will be a key differentiator in the business world of tomorrow. By staying curious, adaptable, and committed to ethical practices, organizations can navigate the complexities of data valuation and harness the full potential of the digital age. The future belongs to those who can see the value hidden in their data – and know how to unlock it.




