Real estate valuation is a cornerstone concept for investors, whether they're directly investing in properties or considering real estate investment trusts (REITs). This in-depth guide will help you grasp the essentials of real estate valuation, its significance in the investment landscape, and how it can influence your portfolio decisions.
What is Real Estate Valuation and Why is it Crucial for Investors?
Real estate valuation is the process of determining the fair market value of a property at a specific point in time. For investors, understanding this concept is vital for several reasons:
- Informed Investment Decisions: Accurate valuation helps you assess whether a property or REIT is overvalued or undervalued.
- Portfolio Diversification: Real estate can be an essential component of a diversified investment portfolio.
- Risk Assessment: Valuation helps in understanding the potential risks associated with real estate investments.
- Performance Measurement: It allows investors to track the performance of their real estate investments over time.
Real-world example: In 2021, Blackstone Group acquired data center operator QTS Realty Trust for $10 billion. The valuation of QTS's assets played a crucial role in determining the acquisition price and assessing the potential return on investment for Blackstone.
Key Approaches to Real Estate Valuation
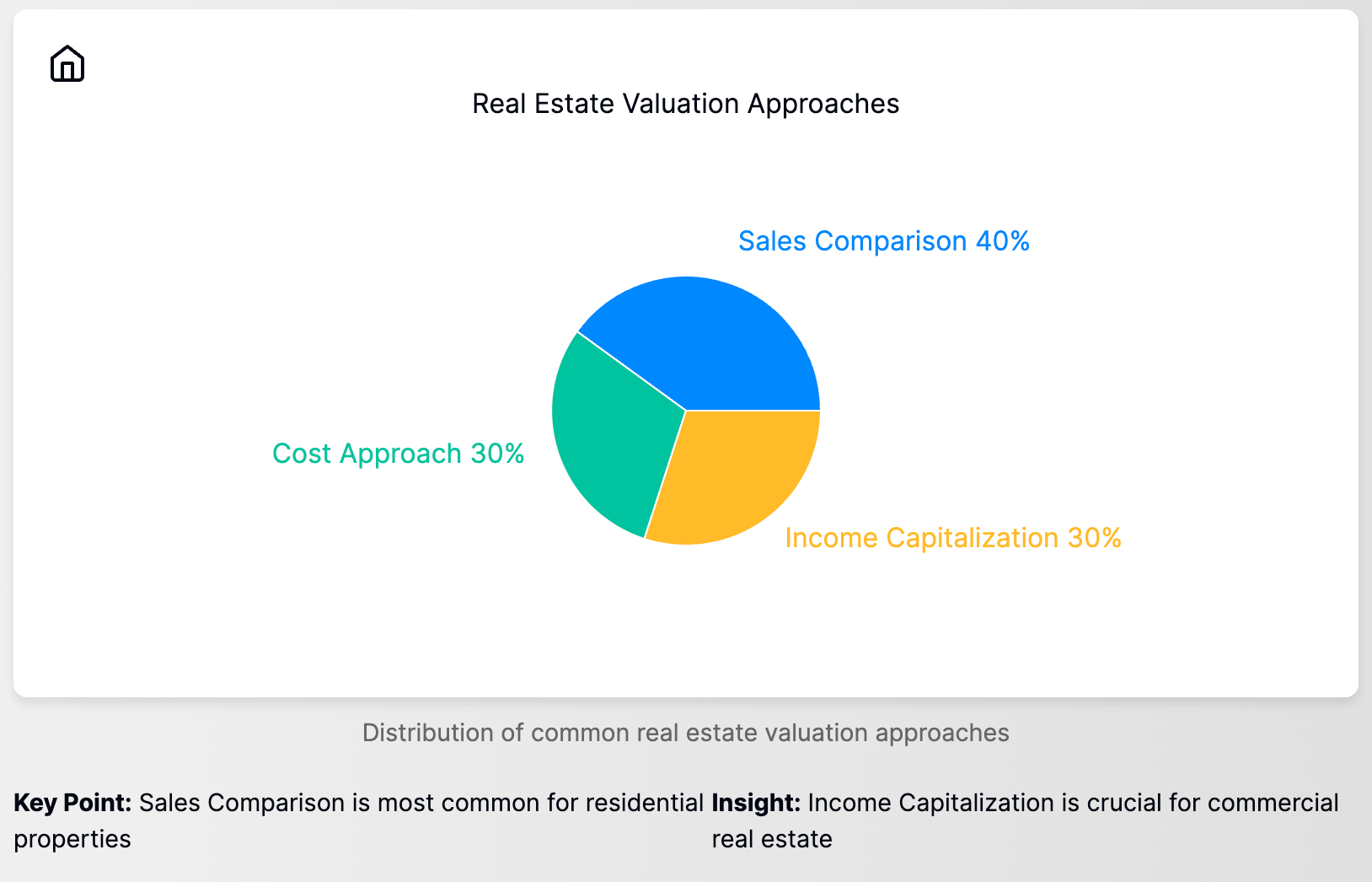
There are three primary approaches to real estate valuation that investors should be familiar with:
1. Sales Comparison Approach
The sales comparison approach, also known as the market approach, involves comparing the subject property to similar properties that have recently sold in the same area. This method is widely used in both residential and commercial real estate valuation.
How it works for investors:
- Analyze recent sales of comparable properties
- Adjust for differences in features, location, and condition
- Determine a fair market value based on these comparisons
The sales comparison method is particularly useful when there are many similar properties in the market. For instance, when valuing a residential REIT like AvalonBay Communities (NYSE: AVB), analysts often use the sales comparison approach to assess the value of individual properties within the REIT's portfolio.
2. Cost Approach
The cost approach estimates the value of a property based on the cost to rebuild or replace it, minus depreciation. This method is often used for new construction or unique properties where comparable sales are scarce.
Key components of the cost approach:
- Land value
- Cost of construction
- Depreciation factors
The cost approach is particularly useful for valuing newly constructed properties. For example, when assessing the value of a newly built logistics facility owned by Prologis (NYSE: PLD), investors might consider the cost approach to understand its true worth.
3. Income Capitalization Approach
This approach is particularly relevant for income-producing properties and is widely used in commercial real estate valuation. It's based on the property's ability to generate income for the investor.
How the income capitalization approach works:
- Estimate the property's net operating income (NOI)
- Determine the appropriate capitalization rate (cap rate)
- Divide NOI by the cap rate to arrive at the property value
Formula: Property Value = Net Operating Income / Capitalization Rate
The income capitalization approach is commonly used when valuing office REITs like Boston Properties (NYSE: BXP). Analysts often use this method to assess the value of their property portfolio based on the income these properties generate.

Factors Influencing Real Estate Valuation
Several key factors can significantly impact real estate valuation:
- Location: Prime locations typically command higher valuations.
- Property Condition: Well-maintained properties generally have higher values.
- Market Trends: Supply and demand dynamics in the local real estate market affect valuation.
- Economic Factors: Interest rates, inflation, and overall economic health play a role.
- Zoning and Land Use Regulations: These can affect a property's potential use and value.
Real-world example: The COVID-19 pandemic significantly impacted real estate valuations across various sectors. For instance, retail REITs like Simon Property Group (NYSE: SPG) saw their valuations drop due to lockdowns and changing consumer behaviors, while industrial properties and REITs like Prologis benefited from the e-commerce boom.
Real Estate Valuation Metrics for Investors
Investors should be familiar with key metrics used in real estate valuation:
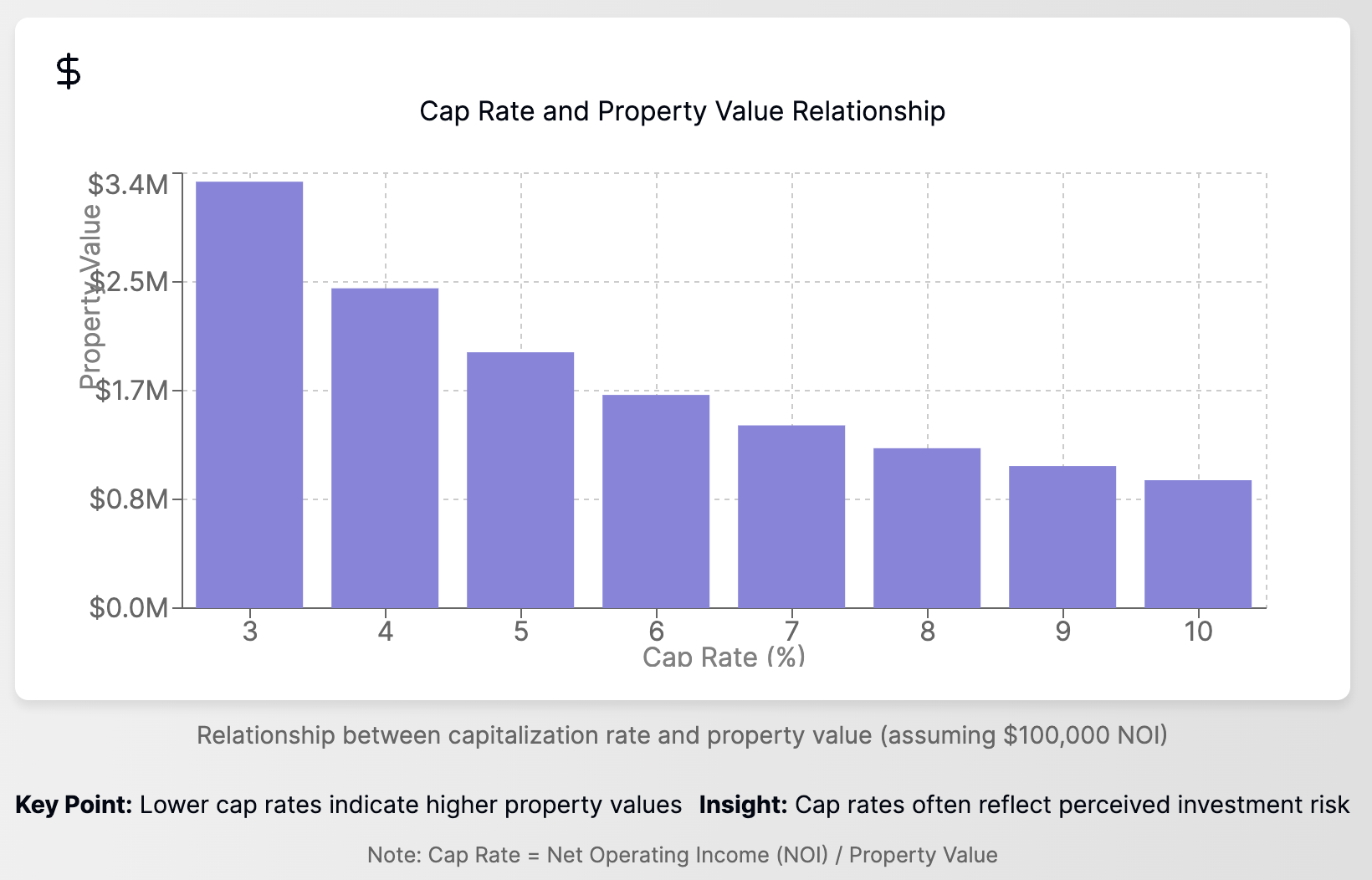
1. Capitalization Rate (Cap Rate)
The cap rate is the ratio of a property's net operating income to its market value. It's a crucial metric in commercial real estate valuation.
Formula: Cap Rate = Net Operating Income / Property Value
A lower cap rate typically indicates a lower risk investment but also a lower yield.
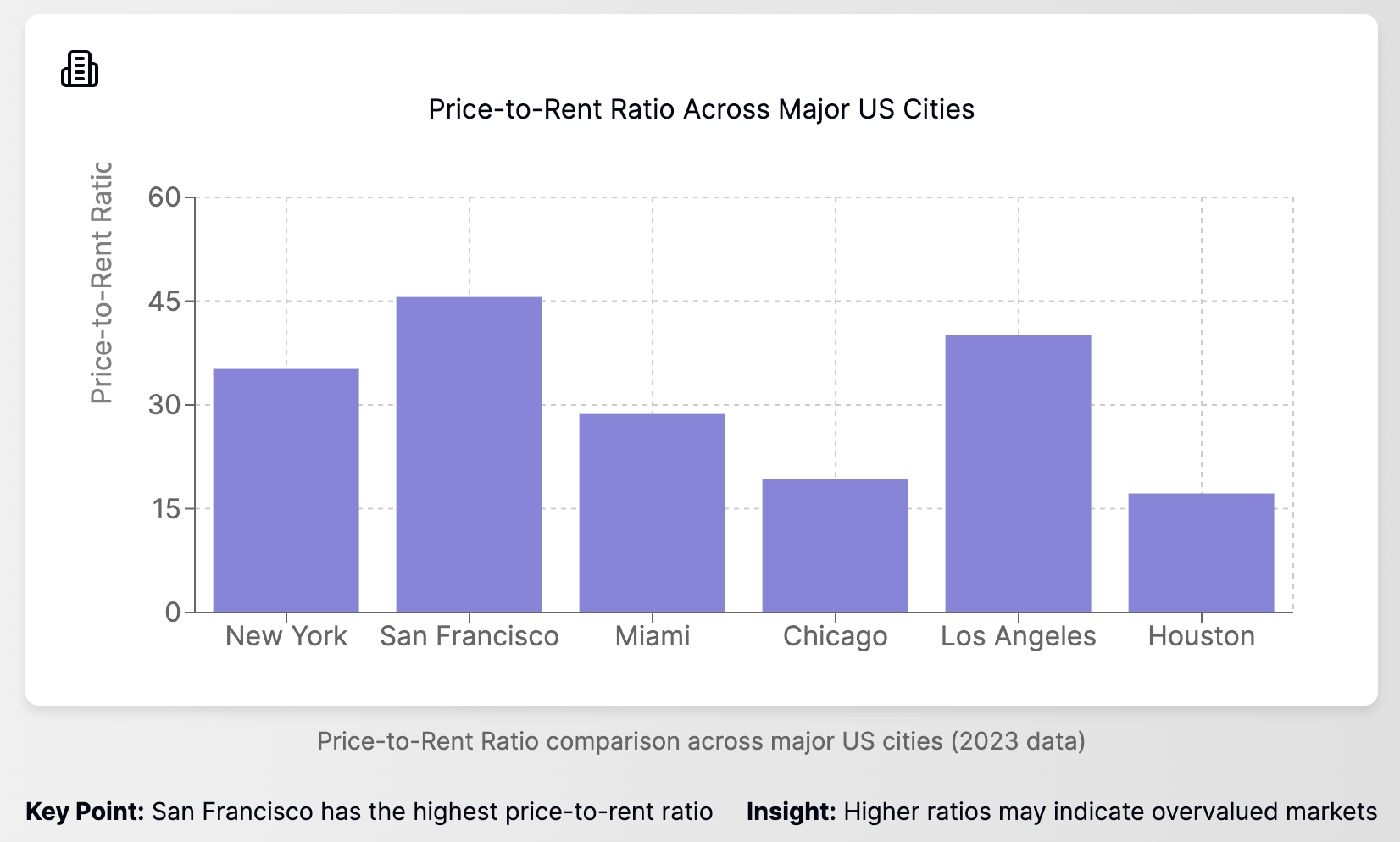
2. Price-to-Rent Ratio
This metric is useful for residential property valuation.
Formula: Price-to-Rent Ratio = Property Price / Annual Rental Income
A high ratio might indicate an overvalued market.
3. Gross Rent Multiplier (GRM)
GRM is used to estimate a property's value based on its gross rental income.
Formula: GRM = Property Price / Annual Gross Rental Income
4. Net Asset Value (NAV)
NAV is particularly important for REIT investors. It represents the total value of a REIT's assets minus its liabilities.
Formula: NAV per Share = (Total Assets - Total Liabilities) / Number of Outstanding Shares
Real-world example: As of Q1 2023, Prologis reported a Net Asset Value per share of $102.65, providing investors with a benchmark to compare against the REIT's market price.

The Role of Professional Appraisers in Real Estate Valuation
While investors can perform basic valuations, professional appraisers play a crucial role in the real estate market:
- Expertise: Appraisers have in-depth knowledge of local markets and valuation methods.
- Objectivity: They provide an unbiased opinion of value.
- Compliance: Appraisers adhere to industry standards and regulations.
- Specialized Valuations: They can handle complex properties or unique situations.
Real-world example: When Brookfield Asset Management acquired Forest City Realty Trust in 2018 for $11.4 billion, professional appraisers played a crucial role in valuing the diverse portfolio of commercial and industrial properties involved in the transaction.
Challenges in Real Estate Valuation
Investors should be aware of several challenges in real estate valuation:
- Market Volatility: Rapid changes in market conditions can affect valuations.
- Lack of Comparable Sales: In unique or rural areas, finding comparable properties can be difficult.
- Subjective Factors: Some aspects of valuation, like property condition, can be subjective.
- Regulatory Changes: Zoning or tax law changes can impact property values.
- Environmental Factors: Issues like climate change risks are increasingly affecting valuations.
Real-world example: Coastal properties in areas prone to rising sea levels, such as parts of Florida, have seen their valuations affected by increased flood risks. This has implications for REITs and investors with significant exposure to these areas.
Valuation Methods for Different Property Types
Different types of properties may require specific valuation approaches:
Residential Properties
For residential properties, the sales comparison approach is often the most relevant. Real estate agents and appraisers typically look at recently sold properties in the same area with similar characteristics.
Commercial Properties
Commercial property valuation often relies heavily on the income capitalization approach. This method is particularly useful for office buildings, retail spaces, and multi-family residential complexes.
Industrial Properties
When valuing industrial properties, a combination of the cost approach and income capitalization approach is often used. The unique nature of many industrial properties can make the sales comparison approach less reliable.

The Importance of Accurate Valuation in Real Estate Transactions
Accurate real estate valuation is crucial in various scenarios:
- Property Sales: Both buyers and sellers rely on accurate valuations to set fair prices.
- Mortgage Lending: Mortgage lenders use property valuations to determine loan amounts.
- Property Taxes: Local governments use property valuations to assess property taxes.
- Investment Analysis: Real estate investors use valuations to make informed investment decisions.
- Insurance: Insurance companies use property valuations to determine coverage amounts.
Frequently Asked Questions About Real Estate Valuation
How do you determine the value of a real estate property?
Determining the value of a real estate property involves several steps:
- Choose the appropriate valuation method (sales comparison, cost approach, or income capitalization).
- Gather relevant data (comparable sales, construction costs, or income and expenses).
- Apply the chosen method to estimate the property's value.
- Consider adjustments for unique features or market conditions.
- Review and refine the valuation based on professional judgment and market knowledge.
What is valuation in real estate?
Valuation in real estate refers to the process of estimating the fair market value of a property. It involves analyzing various factors such as location, property condition, market trends, and economic indicators to determine what a property would likely sell for in the current market.
What is the difference between a valuation and an appraisal?
While the terms are often used interchangeably, there can be subtle differences:
- Valuation: This is a broader term that can refer to any estimate of a property's worth. It can be conducted by various professionals, including real estate agents, investors, or automated valuation models.
- Appraisal: This typically refers to a formal, detailed assessment of a property's value conducted by a licensed or certified appraiser. Appraisals are often required for mortgage lending and follow specific guidelines and standards.
What is the difference between valuation and evaluation in real estate?
- Valuation: This focuses specifically on determining the monetary worth of a property.
- Evaluation: This is a broader term that may include assessing various aspects of a property beyond just its value, such as its condition, potential for improvement, or suitability for a particular use.
Conclusion: Mastering Real Estate Valuation for Investment Success
Understanding real estate valuation is crucial for making informed investment decisions, whether you're investing directly in properties or through REITs. By familiarizing yourself with various valuation approaches, key metrics, and market factors, you can better assess potential investments and manage your real estate portfolio effectively.
Remember that while these principles provide a solid foundation, real estate markets can be complex and dynamic. Stay informed about market trends, economic factors, and regulatory changes that could impact property values. Consider consulting with professional appraisers or financial advisors for more detailed analysis, especially for significant investment decisions.
By mastering the basics of real estate valuation, you'll be better equipped to identify opportunities, manage risks, and optimize your investment strategy in the ever-evolving world of real estate.





