In recent years, Starbucks has faced significant hurdles in its ambitious China expansion strategy, prompting industry experts to call for a reevaluation of the coffee giant's approach in this crucial market. As the company grapples with intensifying local competition, shifting consumer preferences, and economic headwinds, the need for a strategic reassessment has become increasingly apparent. This comprehensive analysis delves into the complexities of Starbucks' operations in China, exploring the challenges, opportunities, and potential paths forward for the global coffee chain.
The Changing Landscape of China's Coffee Market
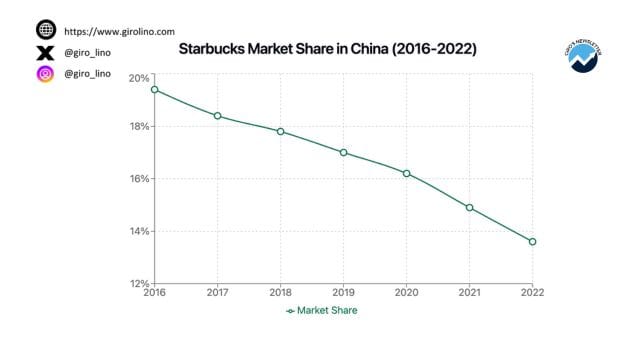
China's coffee market has undergone a dramatic transformation in recent years, evolving from a tea-dominated culture to one where coffee consumption is on the rise. This shift has created both opportunities and challenges for Starbucks, which has long been a dominant player in the Chinese market. However, the landscape is no longer as favorable as it once was, with domestic competitors rapidly gaining ground and changing consumer preferences reshaping the industry.
Before you dive into our in-depth analysis, we have a quick request:
If you find this content useful, please consider sharing it!
Why? Your shares help us reach a wider audience, allowing us to continue producing high-quality, comprehensive content like this—completely free, with no paywalls or subscriptions.
Thank you for your support!
The Rise of Local Competition
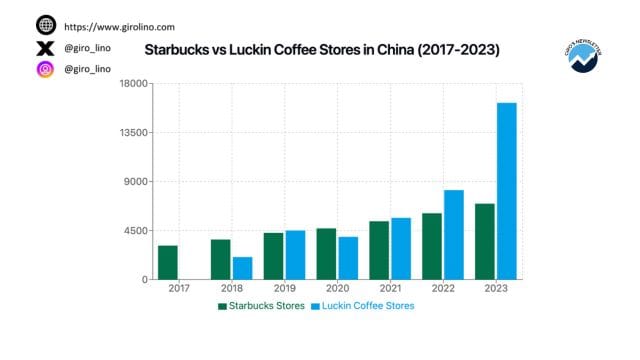
One of the most significant challenges facing Starbucks in China is the meteoric rise of local coffee chains. Companies like Luckin Coffee have disrupted the market with their tech-savvy approach and lower price points, appealing to cost-conscious Chinese consumers. Luckin Coffee, in particular, has experienced explosive growth, surpassing Starbucks in terms of store count with over 10,000 locations across China. This intense competition has eroded Starbucks' market share and forced the company to reassess its pricing strategy and value proposition.
Evolving Consumer Preferences
Chinese consumers, particularly the younger generation, are increasingly favoring local brands and experiences. This shift in consumer behavior presents a unique challenge for Starbucks, which must find ways to maintain its appeal as a Western coffee chain while adapting to local tastes and preferences. The company faces the delicate task of balancing its global brand identity with the need for localization to remain competitive in the Chinese market.
Economic Headwinds and Operational Challenges
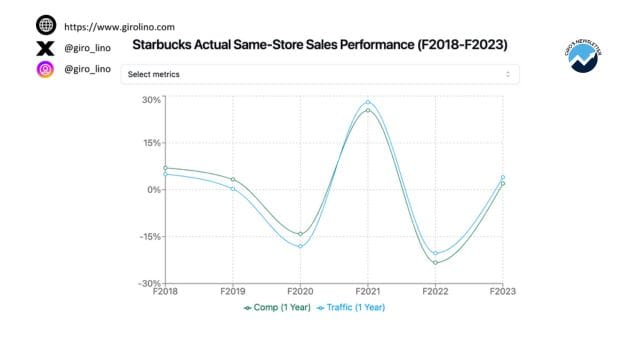
Starbucks' expansion in China has coincided with a period of economic deceleration, which has had a significant impact on consumer spending patterns. This economic slowdown has put pressure on Starbucks' premium positioning, potentially affecting its ability to command higher prices in a market becoming increasingly price-sensitive, affecting SBUX's performance.
Navigating China's Complex Regulatory Environment
Operating in China's intricate regulatory landscape poses ongoing risks for Starbucks. The company must navigate a complex web of government regulations that can impact everything from store locations to product sourcing. This regulatory environment adds an additional layer of complexity to Starbucks' operations and strategic planning in China.
Supply Chain Complexities in a Vast Market
Managing an extensive supply chain across China's vast geography has proven to be a significant operational challenge for Starbucks. Ensuring consistent quality and timely delivery of products to over 6,000 stores spread across more than 230 cities presents logistical hurdles that impact both costs and efficiency. As Starbucks continues to expand, these supply chain challenges are likely to become even more pronounced.
Digital Innovation and Competitive Pressure
In the face of tech-savvy local competitors, Starbucks has been forced to accelerate its digital initiatives in China. Local coffee chains have leveraged advanced digital technologies and delivery services to attract and retain customers, putting pressure on Starbucks to enhance its own digital capabilities. The company's mobile ordering and payment systems in China are among its most advanced globally, but maintaining this edge requires constant innovation and investment.
The Saturation Dilemma
As Starbucks continues its rapid expansion in China, concerns about market saturation in major cities are beginning to surface. This raises questions about the long-term sustainability of the company's aggressive growth strategy. The challenge for Starbucks lies in identifying new growth opportunities while ensuring that its existing stores remain profitable and avoid cannibalizing each other's sales.
Profitability Pressures and Capital Allocation
With increased competition and rising operational costs, Starbucks is facing growing pressure to maintain profitability in its Chinese operations. This has led to calls for a reevaluation of the company's capital expenditure and expansion plans in the country. Investors and analysts are closely watching how Starbucks allocates its resources in China, seeking assurance that the significant investments in the market are delivering adequate returns.
Strategic Reassessment: Charting a Path Forward
In light of these multifaceted challenges, Starbucks finds itself at a critical juncture in its China strategy. The appointment of new CEO Brian Niccol, with his substantial compensation package of $113 million, signals the company's recognition of the need for fresh leadership and strategic thinking to address these issues.
Potential Strategic Adjustments
To navigate the complexities of the Chinese market, Starbucks may need to consider several strategic adjustments:
Slowing Expansion Pace: Reducing the rate of new store openings to focus on optimizing existing locations and ensuring each new store can achieve profitability.
Enhanced Localization Efforts: Increasing initiatives to tailor products, experiences, and marketing to local tastes and preferences to better compete with domestic chains.
Accelerated Digital Innovation: Furthering investments in digital technologies, including mobile ordering and delivery services, to meet evolving consumer expectations and compete effectively with tech-savvy local competitors.
Stringent Cost Management: Implementing more rigorous cost control measures to improve profitability in the face of increased competition and economic pressures.
Strategic Partnerships: Exploring potential collaborations with local entities to enhance market understanding and operational efficiency.
The Importance of China in Starbucks' Global Strategy
Despite the challenges, China remains a crucial market for Starbucks, underscoring the complexity of the company's strategic decisions. As the company's second-largest market globally, China offers significant growth potential, with the country's coffee market projected to grow at a compound annual rate of 10.42% from 2023 to 2028.
Starbucks has successfully positioned itself as a premium brand in China, appealing to the growing middle class and younger consumers who associate the brand with quality and status. The company's early entry and established presence in China provide it with a significant advantage over newer entrants in terms of brand loyalty and market understanding.
Balancing Growth and Adaptation
As Starbucks navigates the complexities of the Chinese market, the company faces the delicate task of balancing its growth ambitions with the need for profitability and adaptability to local market conditions. The decisions made by CEO Brian Niccol regarding the pace of expansion, capital allocation, and strategic initiatives in China will be critical in determining Starbucks' long-term success in this vital market.
The challenges Starbucks faces in China serve as a case study for global brands seeking to expand in complex and rapidly changing markets. By carefully reassessing its strategy and remaining agile in the face of local competition and changing consumer preferences, Starbucks can potentially overcome these hurdles and solidify its position in the Chinese coffee market for years to come.
FAQs About Starbucks' China Expansion Challenges
How many stores does Starbucks currently have in China?
As of 2023, Starbucks operates over 6,000 stores across more than 230 cities in China, making it the company's second-largest market globally.
Who is Starbucks' biggest competitor in China?
Luckin Coffee has emerged as Starbucks' most significant competitor in China, with over 10,000 stores and a tech-driven business model that appeals to local consumers.
What are the main challenges Starbucks faces in the Chinese market?
The primary challenges include intense local competition, changing consumer preferences favoring local brands, economic slowdown, regulatory complexities, and the need for digital innovation to keep pace with tech-savvy competitors.
How is Starbucks adapting its strategy to the Chinese market?
Starbucks is focusing on enhancing its digital capabilities, tailoring products to local tastes, exploring strategic partnerships, and reevaluating its expansion pace to ensure sustainable growth in China.
What is the growth potential for the coffee market in China?
China's coffee market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 10.42% from 2023 to 2028, reaching a market volume of US$17.99 billion by 2028, indicating significant potential for companies like Starbucks.




